Religion and Spirituality's Influences on HIV Syndemics Among MSM: A Systematic Review and Conceptual Model
- PMID: 26319130
- PMCID: PMC4755900
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-015-1173-0
Religion and Spirituality's Influences on HIV Syndemics Among MSM: A Systematic Review and Conceptual Model
Abstract
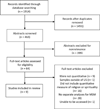
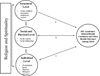
This paper presents a systematic review of the quantitative HIV research that assessed the relationships between religion, spirituality, HIV syndemics, and individual HIV syndemics-related health conditions (e.g. depression, substance abuse, HIV risk) among men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States. No quantitative studies were found that assessed the relationships between HIV syndemics, religion, and spirituality. Nine studies, with 13 statistical analyses, were found that examined the relationships between individual HIV syndemics-related health conditions, religion, and spirituality. Among the 13 analyses, religion and spirituality were found to have mixed relationships with HIV syndemics-related health conditions (6 nonsignificant associations; 5 negative associations; 2 positive associations). Given the overall lack of inclusion of religion and spirituality in HIV syndemics research, a conceptual model that hypothesizes the potential interactions of religion and spirituality with HIV syndemics-related health conditions is presented. The implications of the model for MSM's health are outlined.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; Men who have sex with men; Religion; Spirituality; Syndemics.
Figures
References
-
- CDC. [Accessed 10 Oct 2014];HIV among African American gay and bisexual men. 2014 Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/black_msm_fact_sheet_rev_final.pdf.
-
- Singer M, Clair S. Syndemics and public health: reconceptualizing disease in bio-social context. Med Anthropol Q. 2003;17:423–441. - PubMed
-
- Zinnbauer B, Pargament K, Cole B, Rye M, Butter M, Belavich T, Hipp K, Scott A, Kadar J. Religion and spirituality: unfuzzying the fuzzy. J Sci Study Relig. 1997;36:549–564.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

