Interleukin-7 is required for CD4(+) T cell activation and autoimmune neuroinflammation
- PMID: 26319414
- PMCID: PMC4658267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.08.007
Interleukin-7 is required for CD4(+) T cell activation and autoimmune neuroinflammation
Abstract
IL-7 is known to be vital for T cell homeostasis but has previously been presumed to be dispensable for TCR-induced activation. Here, we show that IL-7 is critical for the initial activation of CD4(+) T cells in that it provides some of the necessary early signaling components, such as activated STAT5 and Akt. Accordingly, short-term in vivo IL-7Rα blockade inhibited the activation and expansion of autoantigen-specific CD4(+) T cells and, when used to treat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), prevented and ameliorated disease. Our studies demonstrate that IL-7 signaling is a prerequisite for optimal CD4(+) T cell activation and that IL-7R antagonism may be effective in treating CD4(+) T cell-mediated neuroinflammation and other autoimmune inflammatory conditions.
Keywords: EAE; IL-7; Signaling pathways; T cells.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
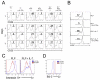


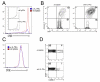
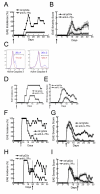
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

