Bile acids: emerging role in management of liver diseases
- PMID: 26320013
- PMCID: PMC4826599
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-015-9656-7
Bile acids: emerging role in management of liver diseases
Abstract
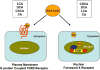
Bile acids are well known for their effects on cholesterol homeostasis and lipid digestion. Since the discovery of bile acid receptors, of which there are farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor, and the plasma membrane G-protein receptor, as well as Takeda G-protein coupled receptor clone 5, further roles have been elucidated for bile acids including glucose and lipid metabolism as well as inflammation. Additionally, treatment with bile acid receptor agonists has shown a decrease in the amount of atherosclerosis plaque formation and decreased portal vascular resistance and portal hypotension in animal models. Furthermore, rodent models have demonstrated antifibrotic activity using bile acid receptor agonists. Early human data using a FXR agonist, obeticholic acid, have shown promising results with improvement of histological activity and even a reduction of fibrosis. Human studies are ongoing and will provide further information on bile acid receptor agonist therapies. Thus, bile acids and their derivatives have the potential for management of liver diseases and potentially other disease states including diabetes and the metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Bile acids; FXR; Liver disease; TGR5.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Dawson PA, Shneider BL, Hofmann AF. Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. 4th. San Diego: Elsevier; 2006. Bile formation and the enterohepatic circulation; pp. 1437–1462.
-
- Agellon LB. Biochemistry of lipids, lipoproteins and membranes. 5th. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2008. Metabolism and function of bile acids; pp. 423–440.
-
- Schiff ER, Dietschy JM. Current concepts of bile acid absorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969;22:273–278. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann AF. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in mammals: form and functions. Front Biosci. 2009;14:2584–2598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

