Effects of inhaled CO administration on acute lung injury in baboons with pneumococcal pneumonia
- PMID: 26320156
- PMCID: PMC4609940
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00240.2015
Effects of inhaled CO administration on acute lung injury in baboons with pneumococcal pneumonia
Abstract
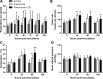
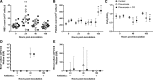
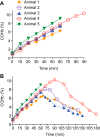
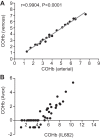
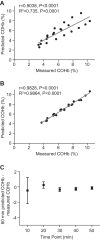
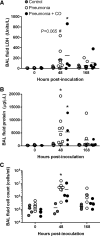
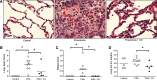
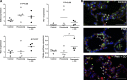
Inhaled carbon monoxide (CO) gas has therapeutic potential for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome if a safe, evidence-based dosing strategy and a ventilator-compatible CO delivery system can be developed. In this study, we used a clinically relevant baboon model of Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia to 1) test a novel, ventilator-compatible CO delivery system; 2) establish a safe and effective CO dosing regimen; and 3) investigate the local and systemic effects of CO therapy on inflammation and acute lung injury (ALI). Animals were inoculated with S. pneumoniae (10(8)-10(9) CFU) (n = 14) or saline vehicle (n = 5); in a subset with pneumonia (n = 5), we administered low-dose, inhaled CO gas (100-300 ppm × 60-90 min) at 0, 6, 24, and/or 48 h postinoculation and serially measured blood carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) levels. We found that CO inhalation at 200 ppm for 60 min is well tolerated and achieves a COHb of 6-8% with ambient CO levels ≤ 1 ppm. The COHb level measured at 20 min predicted the 60-min COHb level by the Coburn-Forster-Kane equation with high accuracy. Animals given inhaled CO + antibiotics displayed significantly less ALI at 8 days postinoculation compared with antibiotics alone. Inhaled CO was associated with activation of mitochondrial biogenesis in the lung and with augmentation of renal antioxidative programs. These data support the feasibility of safely delivering inhaled CO gas during mechanical ventilation and provide preliminary evidence that CO may accelerate the resolution of ALI in a clinically relevant nonhuman primate pneumonia model.
Keywords: Coburn-Forster-Kane equation; Streptococcus pneumoniae; carbon monoxide; drug delivery systems; pneumonia.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Bathoorn E, Slebos DJ, Postma DS, Koeter GH, van Oosterhout AJ, van der Toorn M, Boezen HM, Kerstjens HA. Anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled carbon monoxide in patients with COPD: a pilot study. Eur Respir J 30: 1131–1137, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt WM, Campean V, Kany S, Jurgensen JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Gunzler V, Amann K, Willam C, Wiesener MS, Eckardt KU. Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1970–1978, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

