Critical role of bevacizumab scheduling in combination with pre-surgical chemo-radiotherapy in MRI-defined high-risk locally advanced rectal cancer: Results of the BRANCH trial
- PMID: 26320185
- PMCID: PMC4745808
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4724
Critical role of bevacizumab scheduling in combination with pre-surgical chemo-radiotherapy in MRI-defined high-risk locally advanced rectal cancer: Results of the BRANCH trial
Abstract
Background: We have previously shown that an intensified preoperative regimen including oxaliplatin plus raltitrexed and 5-fluorouracil/folinic acid (OXATOM/FUFA) during preoperative pelvic radiotherapy produced promising results in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). Preclinical evidence suggests that the scheduling of bevacizumab may be crucial to optimize its combination with chemo-radiotherapy.
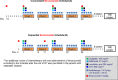
Patients and methods: This non-randomized, non-comparative, phase II study was conducted in MRI-defined high-risk LARC. Patients received three biweekly cycles of OXATOM/FUFA during RT. Bevacizumab was given 2 weeks before the start of chemo-radiotherapy, and on the same day of chemotherapy for 3 cycles (concomitant-schedule A) or 4 days prior to the first and second cycle of chemotherapy (sequential-schedule B). Primary end point was pathological complete tumor regression (TRG1) rate.
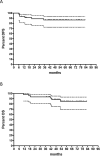
Results: The accrual for the concomitant-schedule was early terminated because the number of TRG1 (2 out of 16 patients) was statistically inconsistent with the hypothesis of activity (30%) to be tested. Conversely, the endpoint was reached with the sequential-schedule and the final TRG1 rate among 46 enrolled patients was 50% (95% CI 35%-65%). Neutropenia was the most common grade ≥ 3 toxicity with both schedules, but it was less pronounced with the sequential than concomitant-schedule (30% vs. 44%). Postoperative complications occurred in 8/15 (53%) and 13/46 (28%) patients in schedule A and B, respectively. At 5 year follow-up the probability of PFS and OS was 80% (95%CI, 66%-89%) and 85% (95%CI, 69%-93%), respectively, for the sequential-schedule.
Conclusions: These results highlights the relevance of bevacizumab scheduling to optimize its combination with preoperative chemo-radiotherapy in the management of LARC.
Keywords: adjuvant chemotherapy; bevacizumab; locally advanced rectal cancer; preoperative chemo-radiotherapy; vessel normalization.
Conflict of interest statement
Antonio Avallone: honoraria from Roche for participation in conferences as speaker and in advisory board meetings. All other authors have declared no conflict interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sauer R, Becker H, Hohenberger W, Rodel C, Wittekind C, Fietkau R, Martus P, Tschmelitsch J, Hager E, Hess CF, Karstens JH, Liersch T, Schmidberger H, Raab R. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1731–1740. - PubMed
-
- Avallone A, Delrio P, Pecori B, Tatangelo F, Petrillo A, Scott N, Marone P, Aloi L, Sandomenico C, Lastoria S, Iaffaioli VR, Scala D, Iodice G, Budillon A, Comella P. Oxaliplatin plus dual inhibition of thymidilate synthase during preoperative pelvic radiotherapy for locally advanced rectal carcinoma: long-term outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;79:670–676. - PubMed
-
- Kozin SV, Boucher Y, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P, Jain RK, Suit HD. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2-blocking antibody potentiates radiation-induced long-term control of human tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2001;61:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, Chung DC, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Kozin SV, Mino M, Cohen KS, Scadden DT, Hartford AC, Fischman AJ, Clark JW, et al. Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med. 2004;10:145–147. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical