Cytosolic Nuclease TREX1 Regulates Oligosaccharyltransferase Activity Independent of Nuclease Activity to Suppress Immune Activation
- PMID: 26320659
- PMCID: PMC4575271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.022
Cytosolic Nuclease TREX1 Regulates Oligosaccharyltransferase Activity Independent of Nuclease Activity to Suppress Immune Activation
Abstract
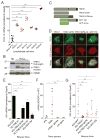
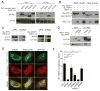
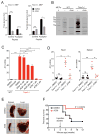
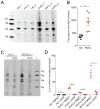
TREX1 is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated negative regulator of innate immunity. TREX1 mutations are associated with autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Biallelic mutations abrogating DNase activity cause autoimmunity by allowing immunogenic self-DNA to accumulate, but it is unknown how dominant frameshift (fs) mutations that encode DNase-active but mislocalized proteins cause disease. We found that the TREX1 C terminus suppressed immune activation by interacting with the ER oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) complex and stabilizing its catalytic integrity. C-terminal truncation of TREX1 by fs mutations dysregulated the OST complex, leading to free glycan release from dolichol carriers, as well as immune activation and autoantibody production. A connection between OST dysregulation and immune disorders was demonstrated in Trex1(-/-) mice, TREX1-V235fs patient lymphoblasts, and TREX1-V235fs knock-in mice. Inhibiting OST with aclacinomycin corrects the glycan and immune defects associated with Trex1 deficiency or fs mutation. This function of the TREX1 C terminus suggests a potential therapeutic option for TREX1-fs mutant-associated diseases.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Exonuclease TREX1 also Has a Sweet Tooth.Immunity. 2015 Sep 15;43(3):411-3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.026. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26377892
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

