Differential Function of Arabidopsis SERK Family Receptor-like Kinases in Stomatal Patterning
- PMID: 26320950
- PMCID: PMC4714584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.07.068
Differential Function of Arabidopsis SERK Family Receptor-like Kinases in Stomatal Patterning
Abstract
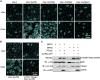
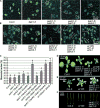
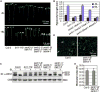
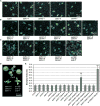
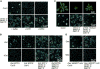
Plants use cell-surface-resident receptor-like kinases (RLKs) to sense diverse extrinsic and intrinsic cues and elicit distinct biological responses. In Arabidopsis, ERECTA family RLKs recognize EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTORS (EPFs) to specify stomatal patterning. However, little is known about the molecular link between ERECTA activation and intracellular signaling. We report here that the SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE (SERK) family RLKs regulate stomatal patterning downstream of EPF ligands and upstream of a MAP kinase cascade. EPF ligands induce the heteromerization of ERECTA and SERK family RLKs. SERK and ERECTA family RLKs transphosphorylate each other. In addition, SERKs associate with the receptor-like protein (RLP) TMM, a signal modulator of stomata development, in a ligand-independent manner, suggesting that ERECTA, SERKs, and TMM form a multiprotein receptorsome consisting of different RLKs and RLP perceiving peptide ligands to regulate stomatal patterning. In contrast to the differential requirement of individual SERK members in plant immunity, cell-death control, and brassinosteroid (BR) signaling, all four functional SERKs are essential but have unequal genetic contributions to stomatal patterning, with descending order of importance from SERK3/BAK1 to SERK2 to SERK1 to SERK4. Although BR signaling connects stomatal development via multiple components, the function of SERKs in stomatal patterning is uncoupled from their involvement in BR signaling. Our results reveal that the SERK family is a shared key module in diverse Arabidopsis signaling receptorsomes and that different combinatorial codes of individual SERK members regulate distinct functions.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interests.
Figures
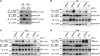

Comment in
-
Stomatal Patterning: SERKs Put the Mouths in Their Right Place.Curr Biol. 2015 Oct 5;25(19):R838-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.08.049. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26439340
References
-
- Li J, Chory J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell. 1997;90:929–938. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T. FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell. 2000;5:1003–1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

