Phosphoenolpyruvate Is a Metabolic Checkpoint of Anti-tumor T Cell Responses
- PMID: 26321681
- PMCID: PMC4567953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.012
Phosphoenolpyruvate Is a Metabolic Checkpoint of Anti-tumor T Cell Responses
Abstract
Activated T cells engage aerobic glycolysis and anabolic metabolism for growth, proliferation, and effector functions. We propose that a glucose-poor tumor microenvironment limits aerobic glycolysis in tumor-infiltrating T cells, which suppresses tumoricidal effector functions. We discovered a new role for the glycolytic metabolite phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in sustaining T cell receptor-mediated Ca(2+)-NFAT signaling and effector functions by repressing sarco/ER Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) activity. Tumor-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells could be metabolically reprogrammed by increasing PEP production through overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (PCK1), which bolstered effector functions. Moreover, PCK1-overexpressing T cells restricted tumor growth and prolonged the survival of melanoma-bearing mice. This study uncovers new metabolic checkpoints for T cell activity and demonstrates that metabolic reprogramming of tumor-reactive T cells can enhance anti-tumor T cell responses, illuminating new forms of immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
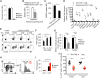


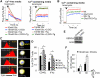
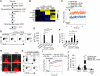
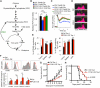
Comment in
-
Nutrient Competition: A New Axis of Tumor Immunosuppression.Cell. 2015 Sep 10;162(6):1206-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.064. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26359979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baitsch L, Fuertes-Marraco SA, Legat A, Meyer C, Speiser DE. The three main stumbling blocks for anticancer T cells. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:364–372. - PubMed
-
- Blagih J, Coulombe F, Vincent EE, Dupuy F, Galicia-Vázquez G, Yurchenko E, Raissi TC, van der Windt GJ, Viollet B, Pearce EL, et al. The energy sensor AMPK regulates T cell metabolic adaptation and effector responses in vivo. Immunity. 2015;42:41–54. - PubMed
-
- Borge PD, Jr., Wolf BA. Insulin receptor substrate 1 regulation of sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 3 in insulin-secreting beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:11359–11368. - PubMed
-
- Braumüller H, Wieder T, Brenner E, Aßmann S, Hahn M, Alkhaled M, Schilbach K, Essmann F, Kneilling M, Griessinger C, et al. T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into senescence. Nature. 2013;494:361–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01AI074699/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074699/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI110613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123350/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063345/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053495/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA168997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P50 CA121974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00CA168997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL108006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 P50 CA121974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI097302/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI110613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA196089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

