Correlation of measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter using ultrasound with magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 26321806
- PMCID: PMC4548416
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.162465
Correlation of measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter using ultrasound with magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Background and aims: Analysis to correlate the measurements of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) obtained by using ultrasound to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques in order to establish the accuracy of ocular sonography as a noninvasive modality for detecting raised intracranial pressure (ICP).
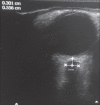
Materials and methods: A prospective, observational study was performed in 100 cases of adult meningoencephalitis patients admitted to Intensive Care Unit in whom MRI was performed for neurodiagnosis. ONSD was measured in such patients, 3 mm behind the globe in each eye. A mean binocular ONSD >4.6 mm in female and 4.8 mm in male was taken as cut-off values for diagnosing raised ICP. This was compared with ONSD measured on T2-weighted MRI image measured 3 mm behind the globe. The reading obtained from both the methods were compared with Bland-Altman analysis for correlation and the findings were tabulated.
Results: The mean ONSD values measured with ultrasonography (USG) and MRI for female were 5.48 ± 0.43 mm and 5.68 ± 0.44 mm and for male were 5.40 ± 0.37 mm and 5.56 ± 0.38 mm, respectively. The mean age of the female and male was 53.90 ± 17.84 and 56.06 ± 15.67 years, respectively. On comparing ultrasound with MRI-derived ONSD values, we found acceptable agreement between both methods for measurements at a depth of 3 mm (r = 0.02, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: In our study, we have found a good correlation between ocular USG and MRI of ONSD. The study has shown agreement with the fact that ocular sonography can be used as a noninvasive tool for detecting raised ICP with accuracy.
Keywords: Intensive Care Unit; magnetic resonance imaging; ocular sonography; optic nerve sheath diameter; raised intracranial pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Accuracy of Ultrasonographically Measured Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Surrogate for the Detection of Intracranial Hypertension Compared to Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measured by MRI: A Prospective Observational Study.Cureus. 2024 Dec 30;16(12):e76655. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76655. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39886717 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter as a marker for evaluation and prognostication of intracranial pressure in Indian patients: An observational study.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2014 Nov;18(11):728-34. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.144015. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25425840 Free PMC article.
-
Use of neuroimaging measurements of optic nerve sheath diameter to assess intracranial pressure in craniosynostosis.Childs Nerv Syst. 2018 May;34(5):939-946. doi: 10.1007/s00381-018-3728-7. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018. PMID: 29380112
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter: present and future perspectives for neurologists and critical care physicians.Neurol Sci. 2019 Dec;40(12):2447-2457. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04015-x. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31367861 Review.
-
Optic Nerve Ultrasound Evaluation in Animals and Normal Subjects.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 5;8:797018. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.797018. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35071277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter with Direct Measurement of Intracranial Pressure through an External Ventricular Drain.Cureus. 2019 Sep 26;11(9):e5777. doi: 10.7759/cureus.5777. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31723536 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Ocular Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Detection of Increased Intracranial Pressure.Front Neurol. 2018 Apr 24;9:278. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00278. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29740393 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Accuracy of Ultrasonographically Measured Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Surrogate for the Detection of Intracranial Hypertension Compared to Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measured by MRI: A Prospective Observational Study.Cureus. 2024 Dec 30;16(12):e76655. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76655. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39886717 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Three Point-of-Care Ultrasound Views and MRI Measurements for Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter: A Prospective Validity Study.Neurocrit Care. 2020 Aug;33(1):173-181. doi: 10.1007/s12028-019-00881-7. Neurocrit Care. 2020. PMID: 31792700
-
Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Assessment in Patients with Intracranial Pressure Monitoring.Cureus. 2018 Nov 5;10(11):e3546. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3546. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 30648078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bäuerle J, Nedelmann M. Sonographic assessment of the optic nerve sheath in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurol. 2011;258:2014–9. - PubMed
-
- Geeraerts T, Merceron S, Benhamou D, Vigué B, Duranteau J. Non-invasive assessment of intracranial pressure using ocular sonography in neurocritical care patients. Intensive Care Med. 2008;34:2062–7. - PubMed
-
- Killer HE, Jaggi GP, Flammer J, Miller NR, Huber AR, Mironov A. Cerebrospinal fluid dynamics between the intracranial and the subarachnoid space of the optic nerve. Is it always bidirectional? Brain. 2007;130(Pt 2):514–20. - PubMed
-
- Hansen HC, Helmke K. Validation of the optic nerve sheath response to changing cerebrospinal fluid pressure: Ultrasound findings during intrathecal infusion tests. J Neurosurg. 1997;87:34–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
