Reliability and Concurrent Validity of Dynamic Rotator Stability Test-A Cross Sectional study
- PMID: 26321818
- PMCID: PMC4551409
Reliability and Concurrent Validity of Dynamic Rotator Stability Test-A Cross Sectional study
Abstract
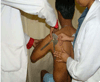
Purpose of the study: To find intra rater and inter rater reliability of Dynamic Rotator Stability Test (DRST) and to find concurrent validity of Dynamic Rotator Stability Test (DRST) with University of Pennsylvania Shoulder Score (PENN) Scale.
Material and method: 40 subjects of either gender between the age group of 18-70 with painful shoulder conditions of musculoskeletal origin was selected through convenient sampling. Tester 1 and tester 2 administered DRST and PENN scale randomly. In a subgroup of 20 subjects DRST was administered by both the testers to find the inter rater reliability. 180° Standard Universal Goniometer was used to take measurements.
Results: For intra-rater reliability, all the test variables were showing highly significant correlation (p=.94 - 1). For inter -rater, with tester 2, test variables like position, ROM, force, direction of abnormal translation, pain during the test, compensatory movement during test were found to be significant (p=.71-1).only some variables of DRST showed significant correlation with PENN scale (P=.320-.450).
Conclusion: Dynamic Rotator Stability Test has good intra rater and moderate inter rater reliability. Concurrent validity of Dynamic Rotator Stability Test was found to be poor when compared to PENN Shoulder Score.
Keywords: Dynamic Rotator Stability Test; Instability; Rotator cuff; Shoulder.
Figures




References
-
- Craig L. Self-management of shoulder disorders—Part 1. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2005;9:189–197.
-
- Goldstein B. Shoulder anatomy and biomechanics. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004;15:313–349. - PubMed
-
- Paul AB, Kevin GL, Eric LS. Mobility and Stability Adaptations in the Shoulder of the Overhead Athlete-A Theoretical and Evidence-Based Perspective. Sports Med. 2008;38:17–36. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
