Activity dependent CAM cleavage and neurotransmission
- PMID: 26321910
- PMCID: PMC4531370
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00305
Activity dependent CAM cleavage and neurotransmission
Abstract
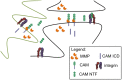
Spatially localized proteolysis represents an elegant means by which neuronal activity dependent changes in synaptic structure, and thus experience dependent learning and memory, can be achieved. In vitro and in vivo studies suggest that matrix metalloproteinase and adamalysin activity is concentrated at the cell surface, and emerging evidence suggests that increased peri-synaptic expression, release and/or activation of these proteinases occurs with enhanced excitatory neurotransmission. Synaptically expressed cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) could therefore represent important targets for neuronal activity-dependent proteolysis. Several CAM subtypes are expressed at the synapse, and their cleavage can influence the efficacy of synaptic transmission through a variety of non-mutually exclusive mechanisms. In the following review, we discuss mechanisms that regulate neuronal activity-dependent synaptic CAM shedding, including those that may be calcium dependent. We also highlight CAM targets of activity-dependent proteolysis including neuroligin and intercellular adhesion molecule-5 (ICAM-5). We include discussion focused on potential consequences of synaptic CAM shedding, with an emphasis on interactions between soluble CAM cleavage products and specific pre- and post-synaptic receptors.
Keywords: CAM; MMP; adhesion; dendritic spine; glutamate; metalloproteases.
Figures
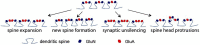
References
-
- Anderson G. R., Galfin T., Xu W., Aoto J., Malenka R. C., Sudhof T. C. (2012). Candidate autism gene screen identifies critical role for cell-adhesion molecule CASPR2 in dendritic arborization and spine development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 18120–18125. 10.1073/pnas.1216398109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

