Simvastatin, atorvastatin, and pravastatin equally improve the hemodynamic status of diabetic rats
- PMID: 26322162
- PMCID: PMC4549667
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i10.1168
Simvastatin, atorvastatin, and pravastatin equally improve the hemodynamic status of diabetic rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate if the effect of statins improving cardiovascular (CV) status of diabetics is drug-specific or class-dependent, and the underlying mechanisms involved.
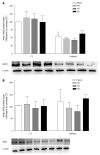
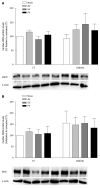
Methods: We compared the results of daily administration over a four-week period of a low dose (10 mg/kg per day) of atorvastatin (AV), simvastatin (SV), and pravastatin (PV) on cardiac performance in diabetic rats. Echocardiographic variables were tested, as well as systolic blood pressure (SBP), acetylcholine (ACh)-induced relaxation, plasma cholesterol levels, and perivascular fibrosis. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxyalkenal (4-HAE), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein levels were also measured in cardiac and aortic homogenates.
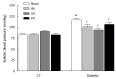
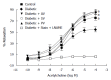
Results: In untreated diabetic rats, cholesterol levels were higher than in control rats (CT; n = 8, P < 0.05), and the low dose of statins used did not modify these levels. In diabetic rats, SBP was higher than in CT, and was significantly reduced by all three statins (n = 10, P < 0.05). Echocardiographic parameters (EF, SV, and COI) were all lower in untreated diabetic rats than in CT (n = 10, P < 0.05). These CV parameters were equally improved by all three statins. The maximal relaxation (EMax) induced by ACh in aortic ring from diabetic rats was also improved. Moreover, this relaxation was abolished by 1 mmol/L NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester, suggesting the involvement of a NO-dependent mechanism.
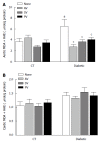
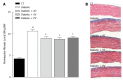
Conclusion: AV, SV, and PV are equally effective in improving CV performance in diabetic rats. All tree statins decreased media thickness, perivascular fibrosis, and both MDA and 4-HAE in the aortas of diabetic rats, without affecting eNOS and iNOS protein levels. The observed hemodynamic benefits are cholesterol-independent. These benefits appear to be secondary to the improved endothelial function, and to the reduced vascular tone and remodeling that result from decreased oxidative stress.
Keywords: Cardiac function; Diabetes; Oxidative stress; Perivascular fibrosis; Statins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Atorvastatin improves systolic function, but does not prevent the development of dilated cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2014 Aug;8(4):133-144. doi: 10.1177/1753944714531065. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 24759610
-
Daily administration of atorvastatin and simvastatin for one week improves cardiac function in type 1 diabetic rats.Pharmacology. 2014;93(1-2):84-91. doi: 10.1159/000358256. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Pharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24556594
-
Effects of chronic treatment with simvastatin on endothelial dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 1999 Jun;17(6):769-76. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199917060-00008. J Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10459874
-
Pioglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, restores endothelial function in aorta of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Apr 1;66(1):150-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.12.025. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15769458
-
Pravastatin sodium activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase independent of its cholesterol-lowering actions.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Jan;33(1):234-41. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00514-2. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999. PMID: 9935036
Cited by
-
The combination of dantrolene and nimodipine effectively reduces 5-HT-induced vasospasms in diabetic rats.Sci Rep. 2021 May 10;11(1):9852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89338-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33972638 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin.J Virol. 2021 Nov 9;95(23):e0139621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01396-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34549987 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of atorvastatin and simvastatin on oxidative stress in diet-induced hyperhomocysteinemia in Wistar albino rats: a comparative study.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Jan;437(1-2):109-118. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3099-5. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28620818
-
Evaluation of the toxicity potential of exercise and atorvastatin/metformin combination therapy on STZ-diabetic rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May;398(5):5989-6007. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03663-x. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39625487
-
Synergistic Effects of Dantrolene and Nimodipine on the Phenylephrine-Induced Contraction and ACh-Induced Relaxation in Aortic Rings from Diabetic Rats.Int J Endocrinol. 2018 Apr 19;2018:9790303. doi: 10.1155/2018/9790303. eCollection 2018. Int J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29849627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002;288:2709–2716. - PubMed
-
- Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:44–84. - PubMed
-
- Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44 Suppl 2:S14–S21. - PubMed
-
- Potenza MA, Gagliardi S, Nacci C, Carratu’ MR, Montagnani M. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: from mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16:94–112. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

