Roles of the canonical myomiRs miR-1, -133 and -206 in cell development and disease
- PMID: 26322174
- PMCID: PMC4549760
- DOI: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i3.162
Roles of the canonical myomiRs miR-1, -133 and -206 in cell development and disease
Abstract
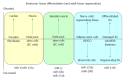
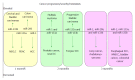
MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that participate in different biological processes, providing subtle combinational regulation of cellular pathways, often by regulating components of signalling pathways. Aberrant expression of miRNAs is an important factor in the development and progression of disease. The canonical myomiRs (miR-1, -133 and -206) are central to the development and health of mammalian skeletal and cardiac muscles, but new findings show they have regulatory roles in the development of other mammalian non-muscle tissues, including nerve, brain structures, adipose and some specialised immunological cells. Moreover, the deregulation of myomiR expression is associated with a variety of different cancers, where typically they have tumor suppressor functions, although examples of an oncogenic role illustrate their diverse function in different cell environments. This review examines the involvement of the related myomiRs at the crossroads between cell development/tissue regeneration/tissue inflammation responses, and cancer development.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell development; MiR-1; MiR-133a; MiR-133b; MiR-206; Muscle microRNAs.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

