Arithmetic and local circuitry underlying dopamine prediction errors
- PMID: 26322583
- PMCID: PMC4567485
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14855
Arithmetic and local circuitry underlying dopamine prediction errors
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Arithmetic and local circuitry underlying dopamine prediction errors.Nature. 2015 Nov 19;527(7578):398. doi: 10.1038/nature15718. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26444234 No abstract available.
Abstract
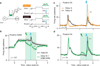
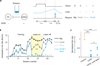
Dopamine neurons are thought to facilitate learning by comparing actual and expected reward. Despite two decades of investigation, little is known about how this comparison is made. To determine how dopamine neurons calculate prediction error, we combined optogenetic manipulations with extracellular recordings in the ventral tegmental area while mice engaged in classical conditioning. Here we demonstrate, by manipulating the temporal expectation of reward, that dopamine neurons perform subtraction, a computation that is ideal for reinforcement learning but rarely observed in the brain. Furthermore, selectively exciting and inhibiting neighbouring GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) neurons in the ventral tegmental area reveals that these neurons are a source of subtraction: they inhibit dopamine neurons when reward is expected, causally contributing to prediction-error calculations. Finally, bilaterally stimulating ventral tegmental area GABA neurons dramatically reduces anticipatory licking to conditioned odours, consistent with an important role for these neurons in reinforcement learning. Together, our results uncover the arithmetic and local circuitry underlying dopamine prediction errors.
Figures
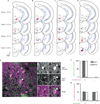
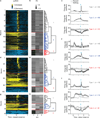
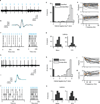
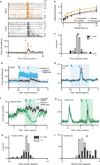

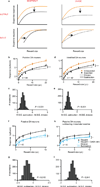
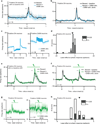

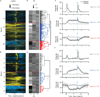
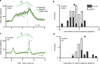
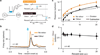
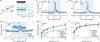
Comment in
-
Systems Neuroscience: Shaping the Reward Prediction Error Signal.Curr Biol. 2015 Nov 16;25(22):R1081-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.09.057. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26583899
References
-
- Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science. 1997;275:1593–1599. - PubMed
-
- Bush RR, Mosteller F. A mathematical model for simple learning. Psychol Rev. 1951;58:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Rescorla RA, Wagner AR. In: Classical conditioning II: current research and theory. Black A, Prokasy W, editors. 1972. pp. 64–99.
Additional references
-
- Bäckman CM, et al. Characterization of a mouse strain expressing Cre recombinase from the 3’ untranslated region of the dopamine transporter locus. Genesis. 2006;44:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nature Neuroscience. 2005;8:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Uchida N, Mainen ZF. Speed and accuracy of olfactory discrimination in the rat. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1224–1229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

