Impaired Vitamin D Signaling in Endothelial Cell Leads to an Enhanced Leukocyte-Endothelium Interplay: Implications for Atherosclerosis Development
- PMID: 26322890
- PMCID: PMC4556440
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136863
Impaired Vitamin D Signaling in Endothelial Cell Leads to an Enhanced Leukocyte-Endothelium Interplay: Implications for Atherosclerosis Development
Abstract
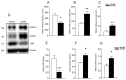
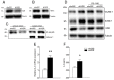
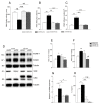
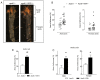
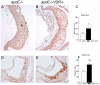
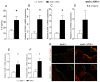
Endothelial cell activation leading to leukocyte recruitment and adhesion plays an essential role in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis. Vitamin D has cardioprotective actions, while its deficiency is a risk factor for the progression of cardiovascular damage. Our aim was to assess the role of basal levels of vitamin D receptor (VDR) on the early leukocyte recruitment and related endothelial cell-adhesion-molecule expression, as essential prerequisites for the onset of atherosclerosis. Knockdown of VDR in endothelial cells (shVDR) led to endothelial cell activation, characterized by upregulation of VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and IL-6, decreased peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) rolling velocity and increased PBMC rolling flux and adhesion to the endothelium. shVDR cells showed decreased IκBα levels and accumulation of p65 in the nucleus compared to shRNA controls. Inhibition of NF-κB activation with super-repressor IκBα blunted all signs of endothelial cell activation caused by downregulation of VDR in endothelial cells. In vivo, deletion of VDR led to significantly larger aortic arch and aortic root lesions in apoE-/- mice, with higher macrophage content. apoE-/-VDR-/-mice showed higher aortic expression of VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and IL-6 when compared to apoE-/-VDR+/+ mice. Our data demonstrate that lack of VDR signaling in endothelial cells leads to a state of endothelial activation with increased leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions that may contribute to the more severe plaque accumulation observed in apoE-/-VDR-/- mice. The results reveal an important role for basal levels of endothelial VDR in limiting endothelial cell inflammation and atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates VCAM-1 expression and NF-κB activation in TNF-α-treated human aortic endothelial cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2011 Feb;22(2):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.01.007. Epub 2010 Jun 22. J Nutr Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20573493
-
Luteolin protects against vascular inflammation in mice and TNF-alpha-induced monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells via suppressing IΚBα/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Nutr Biochem. 2015 Mar;26(3):293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Dec 15. J Nutr Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25577468 Free PMC article.
-
CCL4 Inhibition in Atherosclerosis: Effects on Plaque Stability, Endothelial Cell Adhesiveness, and Macrophages Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 8;21(18):6567. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186567. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32911750 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids and leukocyte-endothelium adhesion: Novel anti-atherosclerotic actions.Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Dec;64:169-181. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Mol Aspects Med. 2018. PMID: 30102930 Review.
-
The association between zinc and endothelial adhesion molecules ICAMs and VCAM-1 and nuclear receptors PPAR-ɑ and PPAR-γ: A systematic review on cell culture, animal and human studies.Microvasc Res. 2021 Nov;138:104217. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104217. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34197877
Cited by
-
Beneficial Role of Vitamin D on Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) in Cardiovascular Diseases.J Lipid Atheroscler. 2022 Sep;11(3):229-249. doi: 10.12997/jla.2022.11.3.229. Epub 2022 Apr 29. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2022. PMID: 36212746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between plasma levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and arterial stiffness in elderly Chinese with non-dipper hypertension: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Feb;99(7):e19200. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019200. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32049858 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of vitamin D supplementation on proatherogenic inflammatory markers and carotid intima media thickness in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial.Endocrine. 2017 Jul;57(1):51-59. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1317-2. Epub 2017 May 16. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 28509078 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of FGF-2 Concentrations with Atheroma Progression in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Apr 6;13(4):577-584. doi: 10.2215/CJN.07980717. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29519952 Free PMC article.
-
The Multiple Effects of Vitamin D against Chronic Diseases: From Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation to Updated Evidence from Clinical Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 30;11(6):1090. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061090. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35739987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vanhoutte PM. Endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 1997;18 Suppl E:E19–29. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

