Immunosuppression With FTY720 Reverses Cardiac Dysfunction in Hypomorphic ApoE Mice Deficient in SR-BI Expression That Survive Myocardial Infarction Caused by Coronary Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 26322923
- PMCID: PMC4703534
- DOI: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000312
Immunosuppression With FTY720 Reverses Cardiac Dysfunction in Hypomorphic ApoE Mice Deficient in SR-BI Expression That Survive Myocardial Infarction Caused by Coronary Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Aims: We recently reported that immunosuppression with FTY720 improves cardiac function and extends longevity in Hypomorphic ApoE mice deficient in scavenger receptor Type-BI expression, also known as the HypoE/SR-BI(–/–) mouse model of diet-induced coronary atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction (MI). In this study, we tested the impact of FTY720 on cardiac dysfunction in HypoE/SR-BI(–/–) mice that survive MI and subsequently develop chronic heart failure.
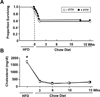
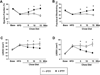
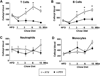
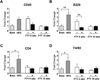
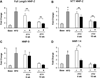
Methods/results: HypoE/SR-BI(–/–) mice were bred to Mx1-Cre transgenic mice, and offspring were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 3.5 weeks to provoke hyperlipidemia, coronary atherosclerosis, and recurrent MIs. In contrast to our previous study, hyperlipidemia was rapidly reversed by inducible Cre-mediated gene repair of the HypoE allele and switching mice to a normal chow diet. Mice that survived the period of HFD were subsequently given oral FTY720 in drinking water or not, and left ventricular (LV) function was monitored using serial echocardiography for up to 15 weeks. In untreated mice, LV performance progressively deteriorated. Although FTY720 treatment did not initially prevent a decline of heart function among mice 6 weeks after Cre-mediated gene repair, it almost completely restored normal LV function in these mice by 15 weeks. Reversal of heart failure did not result from reduced atherosclerosis as the burden of aortic and coronary atherosclerosis actually increased to similar levels in both groups of mice. Rather, FTY720 caused systemic immunosuppression as assessed by reduced numbers of circulating T and B lymphocytes. In contrast, FTY720 did not enhance the loss of T cells or macrophages that accumulated in the heart during the HFD feeding period, but it did enhance the loss of B cells soon after plasma lipid lowering. Moreover, FTY720 potently reduced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and genes involved in innate immunity-associated inflammation in the heart.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that immunosuppression with FTY720 prevents postinfarction myocardial remodeling and chronic heart failure.
Figures


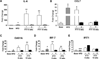
Similar articles
-
The immunosuppressant FTY720 prolongs survival in a mouse model of diet-induced coronary atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;63(2):132-143. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000031. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24508946 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-induced occlusive coronary atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, cardiac dysfunction, and premature death in scavenger receptor class B type I-deficient, hypomorphic apolipoprotein ER61 mice.Circulation. 2005 Jun 28;111(25):3457-64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.523563. Epub 2005 Jun 20. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15967843
-
SR-BI in bone marrow derived cells protects mice from diet induced coronary artery atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e72492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072492. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967310 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I in high-density lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis and heart disease: lessons from gene-targeted mice.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Feb;32(Pt 1):116-20. doi: 10.1042/bst0320116. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 14748727 Review.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
Cited by
-
Searching for Effective Treatments in HFpEF: Implications for Modeling the Disease in Rodents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;16(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/ph16101449. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SR-B1-/-ApoE-R61h/h Mice Mimic Human Coronary Heart Disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Dec;38(6):1123-1137. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07475-8. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 37273155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperglycemia Aggravates Diet-Induced Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial Infarction in SR-B1-Knockout/ApoE-Hypomorphic Mice.Front Physiol. 2018 Oct 9;9:1398. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01398. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30356742 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Molecular Targets Participating in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Cardioprotection.Cardiol Res Pract. 2019 May 28;2019:6935147. doi: 10.1155/2019/6935147. eCollection 2019. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31275641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E and Atherosclerosis: From Lipoprotein Metabolism to MicroRNA Control of Inflammation.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2018 May 23;5(2):30. doi: 10.3390/jcdd5020030. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2018. PMID: 29789495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roberts R, DeMello V, Sobel BE. Deleterious effects of methylprednisolone in patients with myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1976 Mar;53(3 Suppl):I204–I206. - PubMed
-
- Zouggari Y, Ait-Oufella H, Bonnin P, Simon T, Sage AP, Guerin C, Vilar J, Caligiuri G, Tsiantoulas D, Laurans L, Dumeau E, Kotti S, Bruneval P, Charo IF, Binder CJ, Danchin N, Tedgui A, Tedder TF, Silvestre JS, Mallat Z. B lymphocytes trigger monocyte mobilization and impair heart function after acute myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 2013 Oct;19(10):1273–1280. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

