Molecular profiling of activated olfactory neurons identifies odorant receptors for odors in vivo
- PMID: 26322927
- PMCID: PMC4583814
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4104
Molecular profiling of activated olfactory neurons identifies odorant receptors for odors in vivo
Abstract
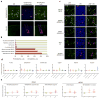
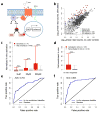
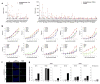
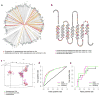
The mammalian olfactory system uses a large family of odorant receptors (ORs) to detect and discriminate amongst a myriad of volatile odor molecules. Understanding odor coding requires comprehensive mapping between ORs and corresponding odors. We developed a means of high-throughput in vivo identification of OR repertoires responding to odorants using phosphorylated ribosome immunoprecipitation of mRNA from olfactory epithelium of odor-stimulated mice followed by RNA-Seq. This approach screened the endogenously expressed ORs against an odor in one set of experiments using awake and freely behaving mice. In combination with validations in a heterologous system, we identified sets of ORs for two odorants, acetophenone and 2,5-dihydro-2,4,5-trimethylthiazoline (TMT), encompassing 69 OR-odorant pairs. We also identified shared amino acid residues specific to the acetophenone or TMT receptors and developed models to predict receptor activation by acetophenone. Our results provide a method for understanding the combinatorial coding of odors in vivo.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

