Differential Expression of Specific Dermatan Sulfate Domains in Renal Pathology
- PMID: 26322947
- PMCID: PMC4556443
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134946
Differential Expression of Specific Dermatan Sulfate Domains in Renal Pathology
Abstract
Dermatan sulfate (DS), also known as chondroitin sulfate (CS)-B, is a member of the linear polysaccharides called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). The expression of CS/DS and DS proteoglycans is increased in several fibrotic renal diseases, including interstitial fibrosis, diabetic nephropathy, mesangial sclerosis and nephrosclerosis. Little, however, is known about structural alterations in DS in renal diseases. The aim of this study was to evaluate the renal expression of two different DS domains in renal transplant rejection and glomerular pathologies. DS expression was evaluated in normal renal tissue and in kidney biopsies obtained from patients with acute interstitial or vascular renal allograft rejection, patients with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IF/TA), and from patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), membranous glomerulopathy (MGP) or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), using our unique specific anti-DS antibodies LKN1 and GD3A12. Expression of the 4/2,4-di-O-sulfated DS domain recognized by antibody LKN1 was decreased in the interstitium of transplant kidneys with IF/TA, which was accompanied by an increased expression of type I collagen, decorin and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), while its expression was increased in the interstitium in FSGS, MGP and SLE. Importantly, all patients showed glomerular LKN1 staining in contrast to the controls. Expression of the IdoA-Gal-NAc4SDS domain recognized by GD3A12 was similar in controls and patients. Our data suggest a role for the DS domain recognized by antibody LKN1 in renal diseases with early fibrosis. Further research is required to delineate the exact role of different DS domains in renal fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


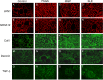

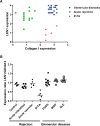
References
-
- Trowbridge JM, Gallo RL. Dermatan sulfate: new functions from an old glycosaminoglycan. Glycobiology. 2002;12(9):117R–25R. - PubMed
-
- Sugahara K, Mikami T, Uyama T, Mizuguchi S, Nomura K, Kitagawa H. Recent advances in the structural biology of chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Current opinion in structural biology. 2003;13(5):612–20. - PubMed
-
- Corsi A, Xu T, Chen XD, Boyde A, Liang J, Mankani M, et al. Phenotypic effects of biglycan deficiency are linked to collagen fibril abnormalities, are synergized by decorin deficiency, and mimic Ehlers-Danlos-like changes in bone and other connective tissues. Journal of bone and mineral research: the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2002;17(7):1180–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

