Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 26323267
- PMCID: PMC6245940
- DOI: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.124
Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Abstract
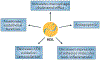
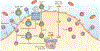
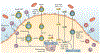
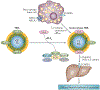
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) protect against atherosclerosis by removing excess cholesterol from macrophages through the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) pathways involved in reverse cholesterol transport. Factors that impair the availability of functional apolipoproteins or the activities of ABCA1 and ABCG1 could, therefore, strongly influence atherogenesis. HDL also inhibits lipid oxidation, restores endothelial function, exerts anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic actions, and exerts anti-inflammatory actions in animal models. Such properties could contribute considerably to the capacity of HDL to inhibit atherosclerosis. Systemic and vascular inflammation has been proposed to convert HDL to a dysfunctional form that has impaired antiatherogenic effects. A loss of anti-inflammatory and antioxidative proteins, perhaps in combination with a gain of proinflammatory proteins, might be another important component in rendering HDL dysfunctional. The proinflammatory enzyme myeloperoxidase induces both oxidative modification and nitrosylation of specific residues on plasma and arterial apolipoprotein A-I to render HDL dysfunctional, which results in impaired ABCA1 macrophage transport, the activation of inflammatory pathways, and an increased risk of coronary artery disease. Understanding the features of dysfunctional HDL or apolipoprotein A-I in clinical practice might lead to new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
R.S.R., H.B.B., B.J.A., P.B., M.J.C., J.W.H., A.K., and A.R.T. declare competing interests. Please see the article online for details. N.R.W. declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenson RS et al. Translation of high-density lipoprotein function into clinical practice: current prospects and future challenges. Circulation 128, 1256–1267 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Rosenson RS et al. HDL measures, particle heterogeneity, proposed nomenclature, and relation to atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. Clin. Chem 57, 392–410 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Du X et al. HDL particle size is a critical determinant of ABCA1-mediated macrophage cellular cholesterol export. Circ. Res 116, 1133–1142 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Riwanto M et al. Altered activation of endothelial anti- and proapoptotic pathways by high-density lipoprotein from patients with coronary artery disease: role of high-density lipoprotein-proteome remodeling. Circulation 127, 891–904 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

