Expression, purification, crystallization and X-ray diffraction studies of the molecular chaperone prefoldin from Homo sapiens
- PMID: 26323306
- PMCID: PMC4555927
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X15013990
Expression, purification, crystallization and X-ray diffraction studies of the molecular chaperone prefoldin from Homo sapiens
Abstract
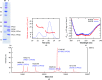
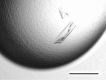
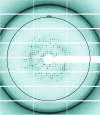
Proper protein folding is an essential process for all organisms. Prefoldin (PFD) is a molecular chaperone that assists protein folding by delivering non-native proteins to group II chaperonin. A heterohexamer of eukaryotic PFD has been shown to specifically recognize and deliver non-native actin and tubulin to chaperonin-containing TCP-1 (CCT), but the mechanism of specific recognition is still unclear. To determine its crystal structure, recombinant human PFD was reconstituted, purified and crystallized. X-ray diffraction data were collected to 4.7 Å resolution. The crystals belonged to space group P21212, with unit-cell parameters a = 123.2, b = 152.4, c = 105.9 Å.
Keywords: molecular chaperone; prefoldin; protein folding.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

