Evaluation of a combinatorial RNAi lentivirus vector targeting foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 26323462
- PMCID: PMC4626173
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4246
Evaluation of a combinatorial RNAi lentivirus vector targeting foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
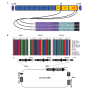
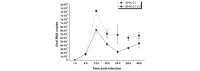
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) causes a highly contagious disease of cloven‑hoofed animals, which leads to serious economical losses. FMDV is not adequately controlled by vaccination or biosecurity measures. To generate genetically modified FMDV‑resistant animals, a combinatorial expression cassette producing three short hairpin (sh)RNAs was constructed using the lentivirus (LV) vector, LV‑3shRNA. The three shRNAs were expressed under the regulation of DNA polymerase III promoters from a buffalo and a bovine source, with one targeted to the non‑structural protein 3B, and the other two targeted to the viral polymerase protein 3D of FMDV, respectively. The role of LV‑3shRNA in the inhibition of the replication of FMDV was determined in BHK‑21 cells and in suckling mice. The results revealed that LV‑3shRNA reduced viral growth 3‑fold (24 h post‑infection) when the cells were challenged with 107‑times the tissue culture infective dose (TCID50)/ml of O serotype FMDV. The suckling mice pretreated with LV‑3shRNA were completely protected on administration of 5‑times the dose of FMDV otherwise sufficient to kill 50% of the experimental animals (LD50). These results demonstrated that the LV‑mediated dual expression of three FMDV‑specific shRNAs provided a novel strategy towards combating FMDV, which facilitates the permanent introduction of novel disease-resistance traits into the buffalo and bovine genomes in the future.
Figures
References
-
- Fasina FO, Connell DR, Talabi OA, Lazarus DD, Adeleke GA, Olusanya TP, Hernandez JA. Foot-and-mouth disease virus strains and examination of exposure factors associated with seropositivity of cattle herds in Nigeria during 2007–2009. Prev Vet Med. 2013;109:334–342. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2012.10.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stram Y, Chai D, Fawzy HE, Molad T, Meiri N, Van-Ham M, el-Kilani S, Fahamy F, Moussa AA, Yadin H. Molecular epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in Israel in 1994 and in other Middle-Eastern countries in the years 1992–1994. Arch Virol. 1995;140:1791–1797. doi: 10.1007/BF01384342. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nampanya S, Khounsy S, Phonvisay A, Young JR, Bush RD, Windsor PA. Financial Impact of Foot and Mouth Disease on Large Ruminant Smallholder Farmers in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2013;6:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Mohapatra JK, Sanyal A, Hemadri D, Tosh C, Kumar RM, Bandyopadhyay SK. Evaluation of in vitro inhibitory potential of small interfering RNAs directed against various regions of foot-and-mouth disease virus genome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;329:1133–1138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.02.080. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

