The many roles of glutamate in metabolism
- PMID: 26323613
- PMCID: PMC4753154
- DOI: 10.1007/s10295-015-1665-y
The many roles of glutamate in metabolism
Abstract
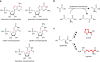
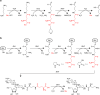
The amino acid glutamate is a major metabolic hub in many organisms and as such is involved in diverse processes in addition to its role in protein synthesis. Nitrogen assimilation, nucleotide, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all utilize glutamate in some manner. Glutamate also plays a role in the catabolism of certain amines. Understanding glutamate's role in these various processes can aid in genome mining for novel metabolic pathways or the engineering of pathways for bioremediation or chemical production of valuable compounds.
Keywords: Lanthipeptides; Lantibiotics; Natural products; Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase; Thiopeptides.
Figures
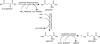

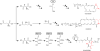

References
-
- Adrian P, Andreux F, Viswanathan R, Freitag D, Scheunert I. Fate of anilines and related compounds in the environment. A review. Toxicol Environ Chem. 1989;20-21:109–120. doi:10.1080/02772248909357366.
-
- Ang EL, Obbard JP, Zhao H. Probing the molecular determinants of aniline dioxygenase substrate specificity by saturation mutagenesis. FEBS J. 2007;274:928–939. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05638.x. - PubMed
-
- Åslund F, Beckwith J. Bridge over troubled waters: Sensing stress by disulfide bond formation. Cell. 1999;96:751–753. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80584-X. - PubMed
-
- Bender DA. Amino acid metabolism. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2012. Nitrogen metabolism. pp. 1–65. doi:10.1002/9781118357514.ch1.
-
- Benigni R, Passerini L. Carcinogenicity of the aromatic amines: from structure–activity relationships to mechanisms of action and risk assessment. Mutat Res. 2002;511:191–206. doi:10.1016/S1383-5742(02)00008-X. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

