Respiratory chest movement measurement as a chair quality indicator--preliminary observations
- PMID: 26323780
- PMCID: PMC4566904
- DOI: 10.1080/10803548.2015.1028224
Respiratory chest movement measurement as a chair quality indicator--preliminary observations
Abstract
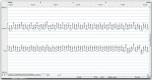
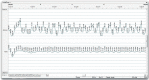
Regardless of the constantly increasing time man is spending in a sitting position, there is still a lack of objective chair quality assessment criteria. The aim of this paper is to find the answer to whether respiratory chest movement measurements can be a chair quality indicator. The study included 34 participants (mean 34.7 years±5.2). Their chest movements were assessed using respiratory inductive plethysmography while sitting on two subsequent chairs. Significant differences in chest movements depending on chair type were observed concerning the breathing duct (upper and lower) and breathing movement amplitude. The amplitude of the upper respiratory track in the first chair was higher (239.4 mV) compared with the second seat (207.3 mV) (p=.018). The analyzed parameters of respiratory chest movement may become a helpful indicator for design and selection of chairs which enable people to both work and relax in the most ergonomic conditions.
Keywords: breath; chair; chest breathing movements; sitting posture.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An office chair to influence the sitting behavior of office workers.Work. 2012;41 Suppl 1:2086-8. doi: 10.3233/WOR-2012-0435-2086. Work. 2012. PMID: 22317024
-
Determination of a sagittal plane axis of rotation for a dynamic office chair.Appl Ergon. 2018 Oct;72:107-112. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2018.05.008. Epub 2018 May 22. Appl Ergon. 2018. PMID: 29885721
-
Sitting comfort of ergonomic office chairs--developed versus intuitive evaluation.Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2010;16(3):369-74. doi: 10.1080/10803548.2010.11076853. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2010. PMID: 20828492 Clinical Trial.
-
Criteria for the ergonomic evaluation of work chairs.Med Lav. 1993 Jul-Aug;84(4):274-85. Med Lav. 1993. PMID: 8255258 Review.
-
Are pressure measurements effective in the assessment of office chair comfort/discomfort? A review.Appl Ergon. 2015 May;48:273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2014.12.010. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Appl Ergon. 2015. PMID: 25683554 Review.
References
-
- Groszek M, Babula G, Nagraba Ł, Stolarczyk A, Mitek T. Risk connected with a wrong sitting position. Arthrosc Jt Surg. 2011;7(3–4):50–61. doi: 10.5604/.969148. - DOI
-
- Leavitt SB, Steward B. Sitting smarter. Health Facil. Manag. 1995;8(6):22. - PubMed
-
- Cybart G. Bóle dolnego odcinka kręgosłupa i miednicy w aspekcie łącznotkankowego mechanizmu przenoszenia bólu. [Pain in lower back and pelvis in terms of connective mechanism for the transmission of pain] Akupunkt Pol. 2000;17/18:564–567.
-
- Janda V. Evaluation of muscular imbalance. In: Liebenson C, editor. Rehabilitation of the spine. Baltimore (MD): Williams and Wilkins; 1996. pp. 319–328.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
