Effects of aging on human leukocytes (part II): immunophenotyping of adaptive immune B and T cell subsets
- PMID: 26324156
- PMCID: PMC5005833
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-015-9829-2
Effects of aging on human leukocytes (part II): immunophenotyping of adaptive immune B and T cell subsets
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Effects of aging on human leukocytes (part II): immunophenotyping of adaptive immune B and T cell subsets.Age (Dordr). 2016 Dec;38(5-6):535-536. doi: 10.1007/s11357-016-9928-8. Age (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 27747451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
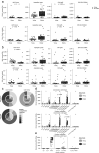
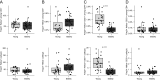
Immunosenescence results from a continuous deterioration of immune responses resulting in a decreased response to vaccines. A well-described age-related alteration of the immune system is the decrease of de novo generation of T and B cells. In addition, the accumulation of memory cells and loss of diversity in antigen specificities resulting from a lifetime of exposure to pathogens has also been described. However, the effect of aging on subsets of γδTCR(+) T cells and Tregs has been poorly described, and the efficacy of the recall response to common persistent infections in the elderly remains obscure. Here, we investigated alterations in the subpopulations of the B and T cells among 24 healthy young (aged 19-30) and 26 healthy elderly (aged 53-67) individuals. The analysis was performed by flow cytometry using freshly collected peripheral blood. γδTCR(+) T cells were overall decreased, while CD4(+)CD8(-) cells among γδTCR(+) T cells were increased in the elderly. Helios(+)Foxp3(+) and Helios(-)Foxp3(+) Treg cells were unaffected with age. Recent thymic emigrants, based on CD31 expression, were decreased among the Helios(+)Foxp3(+), but not the Helios(-)Foxp3(+) cell populations. We observed a decrease in Adenovirus-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells and an increase in CMV-specific CD4(+) T cells in the elderly. Similarly, INFγ(+)TNFα(+) double-positive cells were decreased among activated T cells after Adenovirus stimulation but increased after CMV stimulation. The data presented here indicate that γδTCR(+) T cells might stabilize B cells, and functional senescence might dominate at higher ages than those studied here.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Characterization of γδ T-cells via flow cytometry.Age (Dordr). 2015 Dec;37(6):123. doi: 10.1007/s11357-015-9861-2. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Age (Dordr). 2015. PMID: 26637391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Argentati K, Re F, Donnini A, et al. Numerical and functional alterations of circulating gammadelta T lymphocytes in aged people and centenarians. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;72:65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
