Mass spectrometry imaging reveals new biological roles for choline esters and Tyrian purple precursors in muricid molluscs
- PMID: 26324173
- PMCID: PMC4555103
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13408
Mass spectrometry imaging reveals new biological roles for choline esters and Tyrian purple precursors in muricid molluscs
Abstract
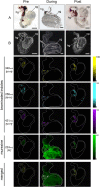
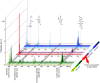
Despite significant advances in chemical ecology, the biodistribution, temporal changes and ecological function of most marine secondary metabolites remain unknown. One such example is the association between choline esters and Tyrian purple precursors in muricid molluscs. Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) on nano-structured surfaces has emerged as a sophisticated platform for spatial analysis of low molecular mass metabolites in heterogeneous tissues, ideal for low abundant secondary metabolites. Here we applied desorption-ionisation on porous silicon (DIOS) to examine in situ changes in biodistribution over the reproductive cycle. DIOS-MSI showed muscle-relaxing choline ester murexine to co-localise with tyrindoxyl sulfate in the biosynthetic hypobranchial glands. But during egg-laying, murexine was transferred to the capsule gland, and then to the egg capsules, where chemical ripening resulted in Tyrian purple formation. Murexine was found to tranquilise the larvae and may relax the reproductive tract. This study shows that DIOS-MSI is a powerful tool that can provide new insights into marine chemo-ecology.
Figures




References
-
- Hay M. E. Marine chemical ecology: What’s known and what’s next? J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 200, 103–134 (1996).
-
- Cummins S. F. et al. Characterization of Aplysia enticin and temptin, two novel water-borne protein pheromones that act in concert with attractin to stimulate mate attraction. J Biol Chem 279, 25614–25622 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Cimino G., Passeggio A., Sodano G., Spinella A. & Villani G. Alarm pheromones from the Mediterranean opisthobranch Haminoea navicula. Experientia 47, 61–63 (1991).
-
- Kelley W. P. et al. Characterization of a novel gastropod toxin (6-Bromo-2-mercaptotryptamine) that inhibits shaker K channel activity. J Biol Chem 278, 34934–34942 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Olivera B. M. et al. Diversity of Conus neuropeptides. Science 249, 257–263 (1990). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

