Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: where do we stand?
- PMID: 26324802
- PMCID: PMC9487695
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.00002915
Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: where do we stand?
Abstract
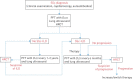
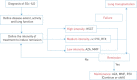
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is common in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients and despite recent advances in the treatment is, at present, the major cause of death. Today, an early diagnosis of ILD is possible, and is mandatory to improve the prognosis of the disease. Pulmonary function tests and high-resolution computed tomography remain the mainstay for the diagnosis of SSc-ILD, but there is a growing interest in lung ultrasound. Recently, the correlation between severity of fibrosis and some peripheral blood biomarkers has been described. Nonselective immunosuppressors are still the main treatment for ILD, with cyclophosphamide (CYC) most widely used to obtain remission. Novel therapies towards specific molecular and cellular targets have been suggested; in particular, rituximab (RTX) has shown promising results, but further research is needed. It is of paramount importance to define the severity of the disease and the risk of progression in order to define the need for treatment and the treatment intensity. We propose the division of the treatment strategies at our disposal to induce remission into three categories: high intensity (haematopoietic stem cell transplantation), medium intensity (CYC and RTX) and low intensity (azathioprine (AZA) and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)). After obtaining remission, maintenance treatment with AZA or MMF should be started. In this review we explore new advances in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of SSc-ILD.
Copyright ©ERS 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Elhai M, Meune C, Avouac J, et al. Trends in mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis over 40 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012; 51: 1017–1026. - PubMed
-
- Rubio-Rivas M, Royo C, Simeón CP, et al. Mortality and survival in systemic sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014; 44: 208–219. - PubMed
-
- Bouros D, Wells AU, Nicholson AG, et al. Histopathologic subsets of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with systemic sclerosis and their relationship to outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 1581–1586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
