Complexity of the human memory B-cell compartment is determined by the versatility of clonal diversification in germinal centers
- PMID: 26324941
- PMCID: PMC4586852
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1511270112
Complexity of the human memory B-cell compartment is determined by the versatility of clonal diversification in germinal centers
Abstract
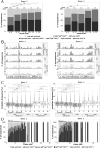
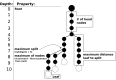
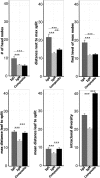
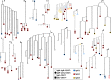
Our knowledge about the clonal composition and intraclonal diversity of the human memory B-cell compartment and the relationship between memory B-cell subsets is still limited, although these are central issues for our understanding of adaptive immunity. We performed a deep sequencing analysis of rearranged immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chain genes from biological replicates, covering more than 100,000 memory B lymphocytes from two healthy adults. We reveal a highly similar B-cell receptor repertoire among the four main human IgM(+) and IgG(+) memory B-cell subsets. Strikingly, in both donors, 45% of sequences could be assigned to expanded clones, demonstrating that the human memory B-cell compartment is characterized by many, often very large, B-cell clones. Twenty percent of the clones consisted of class switched and IgM(+)(IgD(+)) members, a feature that correlated significantly with clone size. Hence, we provide strong evidence that the vast majority of Ig mutated B cells--including IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) B cells--are post-germinal center (GC) memory B cells. Clone members showed high intraclonal sequence diversity and high intraclonal versatility in Ig class and IgG subclass composition, with particular patterns of memory B-cell clone generation in GC reactions. In conclusion, GC produce amazingly large, complex, and diverse memory B-cell clones, equipping the human immune system with a versatile and highly diverse compartment of IgM(+)(IgD(+)) and class-switched memory B cells.
Keywords: IgM memory; IgV gene repertoire; clonal composition; human memory B cell subsets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alt FW, Blackwell TK, Yancopoulos GD. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987;238(4830):1079–1087. - PubMed
-
- MacLennan IC. Germinal centers. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:117–139. - PubMed
-
- Manis JP, Tian M, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of class-switch recombination. Trends Immunol. 2002;23(1):31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

