Inhibition of the oxygen sensor PHD2 in the liver improves survival in lactic acidosis by activating the Cori cycle
- PMID: 26324945
- PMCID: PMC4577207
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1515872112
Inhibition of the oxygen sensor PHD2 in the liver improves survival in lactic acidosis by activating the Cori cycle
Abstract
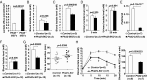
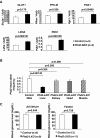
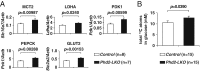
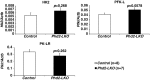
Loss of prolyl hydroxylase 2 (PHD2) activates the hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent hypoxic response, including anaerobic glycolysis, which causes large amounts of lactate to be released from cells into the circulation. We found that Phd2-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) produced more lactate than wild-type MEFs, as expected, whereas systemic inactivation of PHD2 in mice did not cause hyperlacticacidemia. This unexpected observation led us to hypothesize that the hypoxic response activated in the liver enhances the Cori cycle, a lactate-glucose carbon recycling system between muscle and liver, and thereby decreases circulating lactate. Consistent with this hypothesis, blood lactate levels measured after a treadmill or lactate tolerance test were significantly lower in Phd2-liver-specific knockout (Phd2-LKO) mice than in control mice. An in vivo (13)C-labeled lactate incorporation assay revealed that the livers of Phd2-LKO mice produce significantly more glucose derived from (13)C-labeled lactate than control mice, suggesting that blockade of PHD2 in the liver ameliorates lactic acidosis by activating gluconeogenesis from lactate. Phd2-LKO mice were resistant to lactic acidosis induced by injection of a lethal dose of lactate, displaying a significant elongation of survival. Moreover, oral administration of a PHD inhibitor improved survival in an endotoxin shock mice model. These data suggest that PHD2 is a potentially novel drug target for the treatment of lactic acidosis, which is a serious and often fatal complication observed in some critically ill patients.
Keywords: PHD inhibitor; gluconeogenesis; hyperlactatemia; hypoxic response; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kaelin WG, Jr, Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol Cell. 2008;30(4):393–402. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. Oxygen sensing, homeostasis, and disease. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(6):537–547. - PubMed
-
- Epstein AC, et al. C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell. 2001;107(1):43–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

