Thioredoxin 1 mediates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma
- PMID: 26325518
- PMCID: PMC4694848
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4635
Thioredoxin 1 mediates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma
Abstract
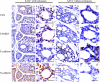
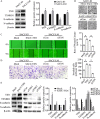
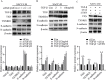
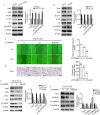
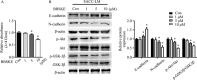
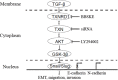
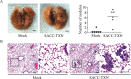
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays an important role in the invasion and metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) which is characterized by wide local infiltration, perineural spread, a propensity to local recurrence and late distant metastasis. Our recent studies have disclosed that TGF-β is a crucial factor for EMT in metastatic SACC. In this study, we further uncovered small redox protein thioredoxin 1 (TXN) as a critical mediator of TGF-β induced EMT. Immunohistochemistry analysis revealed significantly higher expressions of TXN, thioredoxin reductase 1 (TXNRD1) and N-cadherin, and lower expression of E-cadherin in human metastatic SACC compared to non-metastatic SACC tissues. Consistently, cultured SACC cells with stable TXN overexpression had decreased E-cadherin and increased N-cadherin as well as Snail and Slug expressions. The enhanced migration and invasion potential of these cells was abrogated by Akt or TXNRD1 inhibitors. Expression of N-cadherin and Akt p-Akt decreased, whereas E-cadherin expression increased in a BBSKE (TXNRD1 inhibitor)-dose-dependent manner. In a xenograft mouse model, TXN overexpression facilitated the metastatic potential of SACC-83 cells to the lung. Our results indicate that TXN plays a key role in SACC invasion and metastasis through the modulation of TGF-β-Akt/GSK-3β on EMT. TXN could be a potential therapeutic target for SACC.
Keywords: TGF-β; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; metastasis; salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma; thioredoxin 1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-β and epithelial-mesenchymal transition are associated with pulmonary metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2013 Nov;49(11):1051-8. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.07.012. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Oral Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23962790
-
Slug silencing inhibited perineural invasion through regulation of EMMPRIN expression in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):2161-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4043-5. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26349748
-
CDH4 suppresses the progression of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma via E-cadherin co-expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82961-82971. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12821. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27783992 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular features of adenoid cystic carcinoma with an emphasis on microRNA expression.APMIS. 2018 Jun;126 Suppl 140:7-57. doi: 10.1111/apm.12828. APMIS. 2018. PMID: 29924420 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Treatment plan and prognosis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma with lung metastasis].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 1;37(2):214-219. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2019.02.015. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31168990 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of TGFβ-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.J Clin Med. 2016 Jun 29;5(7):63. doi: 10.3390/jcm5070063. J Clin Med. 2016. PMID: 27367735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Trx-1 and S100P promotes colorectal cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by up-regulating S100A4 through AKT activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2430-2441. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13541. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29383839 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects of an Inhibitor of Thioredoxin Reductase on Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β1/Smads Pathway.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 1;8:690170. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.690170. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34540892 Free PMC article.
-
Epiregulin Promotes Lung Metastasis of Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma.Theranostics. 2017 Aug 23;7(15):3700-3714. doi: 10.7150/thno.19712. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29109770 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association analysis for body weight at 35 days measured on 137,343 broiler chickens.Genet Sel Evol. 2021 Sep 8;53(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12711-021-00663-w. Genet Sel Evol. 2021. PMID: 34496773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell D, Hanna EY. Head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma: what is new in biological markers and treatment? Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery. 2013;21:124–129. - PubMed
-
- Rapidis AD, Givalos N, Gakiopoulou H, Faratzis G, Stavrianos SD, Vilos GA, Douzinas EE, Patsouris E. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Clinicopathological analysis of 23 patients and review of the literature. Oral Oncol. 2005;41:328–335. - PubMed
-
- Kokemueller H, Eckardt A, Brachvogel P, Hausamen JE. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck - a 20 years experience. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2004;33:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Kang Y, Massague J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell. 2004;118:277–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

