Sensitivity Analysis of an ENteric Immunity SImulator (ENISI)-Based Model of Immune Responses to Helicobacter pylori Infection
- PMID: 26327290
- PMCID: PMC4556515
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136139
Sensitivity Analysis of an ENteric Immunity SImulator (ENISI)-Based Model of Immune Responses to Helicobacter pylori Infection
Abstract
Agent-based models (ABM) are widely used to study immune systems, providing a procedural and interactive view of the underlying system. The interaction of components and the behavior of individual objects is described procedurally as a function of the internal states and the local interactions, which are often stochastic in nature. Such models typically have complex structures and consist of a large number of modeling parameters. Determining the key modeling parameters which govern the outcomes of the system is very challenging. Sensitivity analysis plays a vital role in quantifying the impact of modeling parameters in massively interacting systems, including large complex ABM. The high computational cost of executing simulations impedes running experiments with exhaustive parameter settings. Existing techniques of analyzing such a complex system typically focus on local sensitivity analysis, i.e. one parameter at a time, or a close "neighborhood" of particular parameter settings. However, such methods are not adequate to measure the uncertainty and sensitivity of parameters accurately because they overlook the global impacts of parameters on the system. In this article, we develop novel experimental design and analysis techniques to perform both global and local sensitivity analysis of large-scale ABMs. The proposed method can efficiently identify the most significant parameters and quantify their contributions to outcomes of the system. We demonstrate the proposed methodology for ENteric Immune SImulator (ENISI), a large-scale ABM environment, using a computational model of immune responses to Helicobacter pylori colonization of the gastric mucosa.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
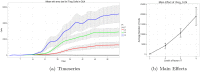
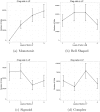

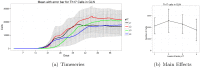

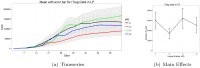
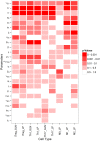
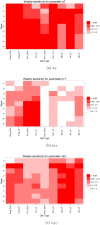
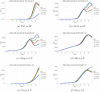


References
-
- Saltelli A, Annoni P, Azzini I, Campolongo F, Ratto M, Tarantola S. Variance based sensitivity analysis of model output Design and estimator for the total sensitivity index. Computer Physics Communications; 2010;.
-
- Helton JC. Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis for Models of Complex Systems In: Computational Methods in Transport: Verification and Validation. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2008.
-
- Cacuci DG, Ionescu-Bujor M, Navon IM. Sensitivity And Uncertainty Analysis: Applications to Large-Scale Systems. Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2005.
-
- Brooks RJ, Semenov MA, Jamieson PD. Simplifying Sirius: sensitivity analysis and development of a meta-model for wheat yield prediction. European Journal of Agronomy. 2001;.
-
- Do H, Rothermel G. Using Sensitivity Analysis to Create Simplified Economic Models for Regression Testing. In: Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

