Asporin Is a Fibroblast-Derived TGF-β1 Inhibitor and a Tumor Suppressor Associated with Good Prognosis in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26327350
- PMCID: PMC4556693
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001871
Asporin Is a Fibroblast-Derived TGF-β1 Inhibitor and a Tumor Suppressor Associated with Good Prognosis in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is a leading malignancy affecting the female population worldwide. Most morbidity is caused by metastases that remain incurable to date. TGF-β1 has been identified as a key driving force behind metastatic breast cancer, with promising therapeutic implications.
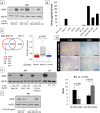
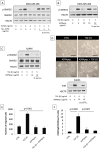
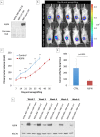
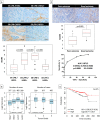
Methods and findings: Employing immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis, we report, to our knowledge for the first time, that asporin is overexpressed in the stroma of most human breast cancers and is not expressed in normal breast tissue. In vitro, asporin is secreted by breast fibroblasts upon exposure to conditioned medium from some but not all human breast cancer cells. While hormone receptor (HR) positive cells cause strong asporin expression, triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells suppress it. Further, our findings show that soluble IL-1β, secreted by TNBC cells, is responsible for inhibiting asporin in normal and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Using recombinant protein, as well as a synthetic peptide fragment, we demonstrate the ability of asporin to inhibit TGF-β1-mediated SMAD2 phosphorylation, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and stemness in breast cancer cells. In two in vivo murine models of TNBC, we observed that tumors expressing asporin exhibit significantly reduced growth (2-fold; p = 0.01) and metastatic properties (3-fold; p = 0.045). A retrospective IHC study performed on human breast carcinoma (n = 180) demonstrates that asporin expression is lowest in TNBC and HER2+ tumors, while HR+ tumors have significantly higher asporin expression (4-fold; p = 0.001). Assessment of asporin expression and patient outcome (n = 60; 10-y follow-up) shows that low protein levels in the primary breast lesion significantly delineate patients with bad outcome regardless of the tumor HR status (area under the curve = 0.87; 95% CI 0.78-0.96; p = 0.0001). Survival analysis, based on gene expression (n = 375; 25-y follow-up), confirmed that low asporin levels are associated with a reduced likelihood of survival (hazard ratio = 0.58; 95% CI 0.37-0.91; p = 0.017). Although these data highlight the potential of asporin to serve as a prognostic marker, confirmation of the clinical value would require a prospective study on a much larger patient cohort.
Conclusions: Our data show that asporin is a stroma-derived inhibitor of TGF-β1 and a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. High asporin expression is significantly associated with less aggressive tumors, stratifying patients according to the clinical outcome. Future pre-clinical studies should consider options for increasing asporin expression in TNBC as a promising strategy for targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular biomarkers for prediction of response to treatment and survival in triple negative breast cancer patients from Egypt.Exp Mol Pathol. 2015 Oct;99(2):303-11. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26232605
-
Elevated TGF-β1 and -β2 expression accelerates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Cytokine. 2015 Sep;75(1):151-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.020. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26088755
-
Asporin is a stromally expressed marker associated with prostate cancer progression.Br J Cancer. 2017 Mar 14;116(6):775-784. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.15. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Br J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28152543 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoprotein asporin as a novel player in tumour microenvironment and cancer progression.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016 Dec;160(4):467-473. doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.037. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016. PMID: 27605398 Review.
-
Expression, regulation and function of asporin, a susceptibility gene in common bone and joint diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(7):724-8. doi: 10.2174/092986708783885237. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18336287 Review.
Cited by
-
Prominin-1-expressing hepatic progenitor cells induce fibrogenesis in murine cholestatic liver injury.Physiol Rep. 2020 Jul;8(14):e14508. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14508. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32686913 Free PMC article.
-
The dual role of asporin in breast cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 9;7(32):52045-52060. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10471. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27409832 Free PMC article.
-
Primordial germ cells as a potential shared cell of origin for mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas and mucinous ovarian tumors.J Pathol. 2018 Dec;246(4):459-469. doi: 10.1002/path.5161. Epub 2018 Oct 19. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30229909 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of bone/cartilage-associated signatures in common fibrotic skin diseases.Front Genet. 2023 Apr 4;14:1121728. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1121728. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37082197 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive investigation of proteoglycan gene expression in breast cancer: Discovery of a unique proteoglycan gene signature linked to the malignant phenotype.Proteoglycan Res. 2025 Jan-Mar;3(1):e70014. doi: 10.1002/pgr2.70014. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Proteoglycan Res. 2025. PMID: 40066261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Wever O, Van Bockstal M, Mareel M, Hendrix A, Bracke M. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts provide operational flexibility in metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;25C:33–46. - PubMed
-
- Shekhar MP, Werdell J, Santner SJ, Pauley RJ, Tait L. Breast stroma plays a dominant regulatory role in breast epithelial growth and differentiation: implications for tumor development and progression. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1320–1326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

