The Spot 42 RNA: A regulatory small RNA with roles in the central metabolism
- PMID: 26327359
- PMCID: PMC4829326
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1086867
The Spot 42 RNA: A regulatory small RNA with roles in the central metabolism
Abstract
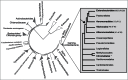
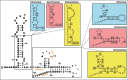
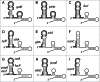
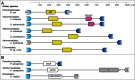
The Spot 42 RNA is a 109 nucleotide long (in Escherichia coli) noncoding small regulatory RNA (sRNA) encoded by the spf (spot fourty-two) gene. spf is found in gamma-proteobacteria and the majority of experimental work on Spot 42 RNA has been performed using E. coli, and recently Aliivibrio salmonicida. In the cell Spot 42 RNA plays essential roles as a regulator in carbohydrate metabolism and uptake, and its expression is activated by glucose, and inhibited by the cAMP-CRP complex. Here we summarize the current knowledge on Spot 42, and present the natural distribution of spf, show family-specific secondary structural features of Spot 42, and link highly conserved structural regions to mRNA target binding.
Keywords: Spot 42; gamma proteobacteria; non-coding RNA; pirin; sRNA; small RNA; spf.
Figures
References
-
- Møller T, Franch T, Udesen C, Gerdes K, Valentin-Hansen P. Spot 42 RNA mediates discoordinate expression of the E. coli galactose operon. Genes Dev 2002; 16:1696-706; PMID:12101127; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.231702 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hansen GA, Ahmad R, Hjerde E, Fenton CG, Willassen NP, Haugen P. Expression profiling reveals Spot 42 small RNA as a key regulator in the central metabolism of Aliivibrio salmonicida. BMC Genomics 2012; 13:37; PMID:22272603; http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-37 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ikemura T, Dahlberg JE. Small ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. I. Characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Biol Chem 1973; 248:5024-32; PMID:4577761 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
