Contrast enhanced computed tomography and reconstruction of hepatic vascular system for transjugular intrahepatic portal systemic shunt puncture path planning
- PMID: 26327770
- PMCID: PMC4548123
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9623
Contrast enhanced computed tomography and reconstruction of hepatic vascular system for transjugular intrahepatic portal systemic shunt puncture path planning
Abstract
Aim: To describe a method for the transjugular intrahepatic portal systemic shunt (TIPS) placement performed with the aid of contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) and three-dimensional reconstructed vascular images (3D RVIs), and to assess its safety and effectiveness.
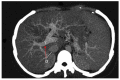
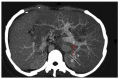
Methods: Four hundred and ninety patients were treated with TIPS between January 2005 and December 2012. All patients underwent liver CECT and reconstruction of 3D RVIs of the right hepatic vein to portal vein (PV) prior to the operation. The 3D RVIs were carefully reviewed to plan the puncture path from the start to target points for needle pass through the PV in the TIPS procedure.
Results: The improved TIPS procedure was successful in 483 (98.6%) of the 490 patients. The number of punctures attempted was one in 294 (60%) patients, 2 to 3 in 147 (30%) patients, 4 to 6 in 25 (5.1%) patients and more than 6 in 17 (3.5%) patients. Seven patients failed. Of the 490 patients, 12 had punctures into the artery, 15 into the bile duct, eight into the gallbladder, and 18 through the liver capsule. Analysis of the portograms from the 483 successful cases indicated that the puncture points were all located distally to the PV bifurcation on anteroposterior images, while the points were located proximally to the bifurcation in the three cases with intraabdominal bleeding. The complications included three cases of bleeding, of whom one died and two needed surgery.
Conclusion: Use of CECT and 3D RVIs to plan the puncture path for TIPS procedure is safe, simple and effective for clinical use.
Keywords: 3D vascular reconstruction; Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; Interventional radiology; Transjugular intrahepatic portal systemic shunt.
Figures


References
-
- Liu J, Fan D. Hepatitis B in China. Lancet. 2007;369:1582–1583. - PubMed
-
- Rösch J, Uchida BT, Putnam JS, Buschman RW, Law RD, Hershey AL. Experimental intrahepatic portacaval anastomosis: use of expandable Gianturco stents. Radiology. 1987;162:481–485. - PubMed
-
- Rössle M, Richter GM, Nöldge G, Palmaz JC, Wenz W, Gerok W. New non-operative treatment for variceal haemorrhage. Lancet. 1989;2:153. - PubMed
-
- Wells LB, Mangat K, Gupte GL. Role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in children with advanced intestinal failure associated liver disease and portal hypertension. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;60:e38–e39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

