Triterpenoid Saponin W3 from Anemone flaccida Suppresses Osteoclast Differentiation through Inhibiting Activation of MAPKs and NF-κB Pathways
- PMID: 26327814
- PMCID: PMC4551756
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.12296
Triterpenoid Saponin W3 from Anemone flaccida Suppresses Osteoclast Differentiation through Inhibiting Activation of MAPKs and NF-κB Pathways
Abstract
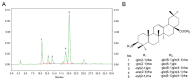
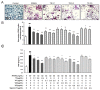
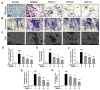
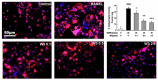
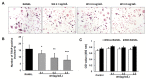
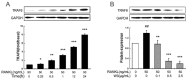
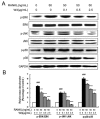
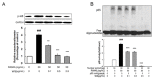
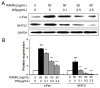
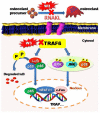
Excessive bone resorption by osteoclasts within inflamed joints is the most specific hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis. A. flaccida has long been used for the treatment of arthritis in folk medicine of China; however, the active ingredients responsible for the anti-arthritis effects of A. flaccida are still elusive. In this study, W3, a saponin isolated from the extract of A. flaccida was identified as the major active ingredient by using an osteoclast formation model induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL). W3 dose-dependently suppressed the actin ring formation and lacunar resorption. Mechanistic investigation revealed that W3 inhibited the RANKL-induced TRAF6 expression, decreased phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and IκB-α, and suppressed NF-κB p65 DNA binding activity. Furthermore, W3 almost abrogated the expression of c-Fos and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATc1). Therefore, our results suggest that W3 is a potential agent for treating lytic bone diseases although further evaluation in vivo and in clinical trials is needed.
Keywords: Anemone flaccida; Bone resorption; Osteoclasts; RANKL.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Total saponin from Anemone flaccida Fr. Schmidt abrogates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption via the inhibition of RANKL-induced NF-κB, JNK and p38 MAPKs activation.J Transl Med. 2015 Mar 15;13:91. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0440-1. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25889035 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand–induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and Ca2+–nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Jun;27(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1576. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22337253
-
Maslinic acid suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss by regulating RANKL-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26(3):644-56. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.242. J Bone Miner Res. 2011. PMID: 20814972
-
[Research progress of studies on chemical constituents and biologic activities of Anemone species].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Mar;44(5):912-919. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181226.011. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30989849 Review. Chinese.
-
Review of Anemone raddeana Rhizome and its pharmacological effects.Chin J Integr Med. 2018 Jan;24(1):72-79. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2901-2. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Chin J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 28986812 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant PDA-PEG nanoparticles alleviate early osteoarthritis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis in subchondral bone.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Nov 16;20(1):479. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01697-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36384720 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of N-[2-(4-acetyl-1-piperazinyl) phenyl]-2-(2-chlorophenoxy) acetamide on Osteoclast Differentiation In Vitro via the Downregulation of TRAF6.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 20;20(20):5196. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205196. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31635168 Free PMC article.
-
Appropriate Reference Genes for RT-qPCR Normalization in Various Organs of Anemone flaccida Fr. Schmidt at Different Growing Stages.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 23;12(3):459. doi: 10.3390/genes12030459. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807101 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Sea Tangle (Laminaria japonica Aresch) Suppresses RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Scavenging ROS in RAW 264.7 Cells.Foods. 2019 Jul 26;8(8):290. doi: 10.3390/foods8080290. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31357503 Free PMC article.
-
Anemone medicinal plants: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and biology.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017 Mar;7(2):146-158. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017. PMID: 28303220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337–342. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S, Okada Y. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation. Current drug targets Inflammation and allergy. 2005;4(3):325–328. - PubMed
-
- Han LT, Li J, Huang F, Yu SG, Fang NB. Triterpenoid saponins from Anemone flaccida induce apoptosis activity in HeLa cells. Journal of Asian natural products research. 2009;11(2):122–127. - PubMed
-
- Bing F, Zhang G, Deng C, Gong Y. Immune mechanisms of Wugong Sanqi extract against CIA in mouse. Chinese Journal of Immunology. 2008;24(8):716–720.
-
- Cheng S, Du Y, Bing F, Zhang G. Synthesis of flaccidoside II, a bidesmosidic triterpene saponin isolated from Chinese folk medicine Di Wu. Carbohydrate research. 2008;343(3):462–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

