Facial Onset Sensory and Motor Neuronopathy: Further Evidence for a TDP-43 Proteinopathy
- PMID: 26327906
- PMCID: PMC4448067
- DOI: 10.1159/000381944
Facial Onset Sensory and Motor Neuronopathy: Further Evidence for a TDP-43 Proteinopathy
Abstract
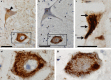
Three patients with the clinical and investigation features of facial onset sensory and motor neuronopathy (FOSMN) syndrome are presented, one of whom came to a post-mortem examination. This showed TDP-43-positive inclusions in the bulbar and spinal motor neurones as well as in the trigeminal nerve nuclei, consistent with a neurodegenerative pathogenesis. These data support the idea that at least some FOSMN cases fall within the spectrum of the TDP-43 proteinopathies, and represent a focal form of this pathology.
Keywords: Facial onset sensory and motor neuronopathy; Motor neurone disease; TDP-43 proteinopathy.
Figures
References
-
- Vucic S, Tian D, Chong PS, et al. Facial onset sensory and motor neuronopathy (FOSMN syndrome): a novel syndrome in neurology. Brain. 2006;129:3384–3390. - PubMed
-
- Vucic S, Stein TD, Hedley-White ET, et al. FOSMN syndrome: novel insight into disease pathophysiology. Neurology. 2012;79:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Isoardo G, Troni W. Sporadic bulbospinal muscle atrophy with facial-onset sensory neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2008;37:659–662. - PubMed
-
- Hokonohara T, Shigeto H, Kawano Y, Ohyagi Y, Uehara M, Kira J. Facial onset sensory and motor neuronopathy (FOSMN) syndrome responding to immunotherapies. J Neurol Sci. 2008;275:157–158. - PubMed
-
- Fluchere F, Verschueren A, Cintas P, et al. Clinical features and follow-up of four new cases of facial-onset sensory and motor neuronopathy. Muscle Nerve. 2011;43:136–140. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

