Photorefractive Keratectomy in Keratoconus
- PMID: 26327912
- PMCID: PMC4553919
- DOI: 10.1159/000431306
Photorefractive Keratectomy in Keratoconus
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the efficacy and safety of topography-guided photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) for keratoconus and to estimate the subsequent risk of progression.
Methods: This is a retrospective follow-up study. Between 1998 and 2013, 28 eyes of 23 patients (age 17-60) with grade 1-3 keratoconus received topography-guided PRK. Corrected-distance visual acuity (CDVA), keratometry, pachymetry, and corneal topography were assessed before, after 3 months, and at a late follow-up of a median of 7 years after the procedure. Postoperative complications including subsequent keratoplasty were noted.
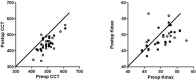
Results: Of the 28 eyes, 5 (18%percnt;) had undergone corneal transplantation at a median of 7 years (range 3-10) after PRK. Four eyes were not available for follow-up. In the remaining 19 eyes, CDVA was improved in 16 eyes (84.3%percnt;), reduced in 2 eyes (10.5%percnt;), and unchanged in 1 eye (5.2%percnt;). Thus, average CDVA had improved from 0.49 logMAR before PRK to 0.27 logMAR at 3 months, and to 0.24 at the long-term follow-up. The mean spherical equivalent was reduced from - 6.2 to -3.7 dpt after 3 months and to -2.1 dpt at the late follow-up. Similarly, the mean cylinder was reduced from -4.2 to -3.0 dpt after 3 months and at the late follow-up.
Conclusion: Topography-guided PRK in keratoconus may be effective for reducing myopia and astigmatism and may offer a temporary or permanent alternative to keratoplasty in contact lens-intolerant keratoconus. In the present study, we found a low risk of keratoconus progression after PRK.
Keywords: Keratoconus; Photorefractive keratectomy; Refractive surgical procedures.
Figures

References
-
- Fadlallah A, Dirani A, EI Rami H, Cherfane G, Jarade E. Safety and visual outcome of Visian toric ICL implantation after corneal collagen cross-linking in keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2013;29:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt-Bernard CF, Lesage C, Arnaud B. Keratectasia induced by laser in situ keratomileusis in keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2000;16:368–370. - PubMed
-
- Dawson DG, Randleman JB, Grossniklaus HE, et al. Corneal ectasia after excimer laser keratorefractive surgery: histopathology, ultrastructure, and pathophysiology. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:2181–2191. - PubMed
-
- Bilgihan K, Ozdek SC, Konuk O, Akata F, Hasanreisoglu B. Results of photorefractive keratectomy in keratoconus suspects at 4 years. J Refract Surg. 2000;16:438–443. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

