Expression of epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 correlates with clinicopathological features of osteosarcoma
- PMID: 26328008
- PMCID: PMC4548316
Expression of epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 correlates with clinicopathological features of osteosarcoma
Abstract
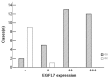
Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 gene (EGFL7) encodes an angiogenesis related factor and plays a crucial role in many human cancers. Previous studies have suggestedthat EGFL7 acts as a facilitator for tumor angiogenesis. However, little is known as to its role in osteosarcoma. Our aim was to investigate the expression of EGFL7 and to explore its correlation with the clinicopathological features of osteosarcoma. Tumor tissues from 32 Chinese young patients (below age of 24) with osteosarcoma were collected and subjected to EGFL7 detection by immunohistochemistry. The tissues from 10 patients with osteochondroma were collected and analyzed as controls. The intratumoral microvessel density (MVD) was examined by immunohistochemical staining using CD34 antibody. The results showed that patients with osteosarcoma had higher levels of EGFL7 in the tumor tissues compared to patients with osteochondroma (p<0.001). The expression of EGFL7 was significantly higher in advanced osteosarcoma (Enneking IIB-III) than that in early tumor stage (Enneking IA-IIA) (p<0.01). There is also a significant correlation between increased expression of EGFL7 and the Enneking stage (R = 0.714, p<0.001). Moreover, we detected a higher level of EGFL7 expression in tumor tissues of patients with recurrent or metastatic (bone or lung) osteosarcoma than those without recurrence or metastasis after 3 years' follow-up (p<0.01). There is no detectable difference of EGFL7 expression between tumor tissues from different tumor location and sex. Finally, we showed that high level of EGFL7expression was significantly correlated with high MVD (R = 0.829, p<0.001). In conclusion, our study demonstrates for the first time that there was a tumor grade-dependent up-regulation of EGFL7 in osteosarcoma. Elevated EGFL7 expression correlated with poor clinical outcome: i.e. advanced tumor stage, recurrent and metastatic osteosarcoma. Our findings support EGFL7 as a potential prognostic marker, and may provide novel insights for the diagnostics and therapeutics of osteosarcoma.
Keywords: Osteosarcoma; clinicopathology; epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 (EGFL7); microvessel density (MVD); prognosis; tumor angiogenesis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel Expression of EGFL7 in Osteosarcoma and Sensitivity to Cisplatin.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 6;10:74. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00074. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117731 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 in pancreatic cancer.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2014 Oct;13(5):523-8. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(14)60272-1. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2014. PMID: 25308363
-
Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 promotes cell invasion and angiogenesis in pancreatic carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Feb;77:167-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 26796281
-
EGFL7: Master regulator of cancer pathogenesis, angiogenesis and an emerging mediator of bone homeostasis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Nov;233(11):8526-8537. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26792. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29923200 Review.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of EGFL7 in Cancer and Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 1;13(5):1014. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051014. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Attenuation of EGFL7 Expression Inhibits Growth Hormone-Producing Pituitary Adenomas Growth and Invasion.Hum Gene Ther. 2018 Apr 2;29(12):1396-406. doi: 10.1089/hum.2017.200. Online ahead of print. Hum Gene Ther. 2018. PMID: 29466872 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Expression of EGFL7 in Osteosarcoma and Sensitivity to Cisplatin.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 6;10:74. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00074. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117731 Free PMC article.
-
Effect and Mechanism of EGFL7 Downregulation in Human Osteosarcoma Cells on the Biological Function of Co-cultured HUVEC.Balkan Med J. 2018 Mar 15;35(2):155-162. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0045. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Balkan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29363485 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor microenvironment of metastatic osteosarcoma in the human and canine lung.Commun Biol. 2025 May 15;8(1):756. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07992-2. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40374715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals differential expression of EGFL7 and VEGF in giant-cell tumor of bone and osteosarcoma.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Jul;247(14):1214-1227. doi: 10.1177/15353702221088238. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35695550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Tang XD, Guo W, Yang R, Yang Y, Ji T. Limb salvage surgery for osteosarcoma around the knee in children and adolescent patients. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007;45:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Gazitt Y, Kolaparthi V, Moncada K, Thomas C, Freeman J. Targeted therapy of human osteosarcoma with 17AAG or rapamycin: characterization of induced apoptosis and inhibition of mTOR and Akt/MAPK/Wnt pathways. Int J Oncol. 2009;34:551–561. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
