Current use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors in urology
- PMID: 26328208
- PMCID: PMC4548666
- DOI: 10.5152/tud.2015.46354
Current use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors in urology
Abstract
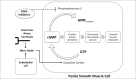
The causes of male erectile dysfunction (ED) are quite variable and are now commonly divided into etiologies such as ischemia, smooth muscle damage, or altered blood flow. Although varying rates of ED have been reported in literature, the number of men with ED is projected to increase worldwide by 2025 to approximately 322 million. Since the introduction of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, there has been a paradigm shift in the treatment of ED because PDE5 inhibitors address a broad spectrum of etiologies for ED. Today, the American Urological Association recommends the use of three PDE5 inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil) as a first-line therapy for the treatment of ED. This review evaluates the pharmacological mechanism of PDE5 inhibitors along with the impact and use of sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, and avanafil. By increasing intracellular cGMP levels, PDE5 inhibitors have been shown to be effective in the treatment of ED. Through their effects on other cellular signaling pathways, PDE5 inhibitors have the potential for treating other urologic conditions as well. The use of PDE5 inhibitors can also be combined to produce a synergistic effect in conditions such as male hypogonadism and benign prostatic hyperplasia in addition to ED.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; PDE5 inhibitors; sildenafil.
References
-
- Setter SM, Iltz JL, Fincham JE, Campbell RK, Baker DE. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39:1286–95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1345/aph.1E487. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lue TF, Hon S. Pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Campbell-Walsh Urology. 2000:688–70.
-
- Houry SK, Harlip IS. Sexual medicine sexual dysfunction in men and women. 2010:19–22.
-
- Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00142.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crowe SM, Streetman DS. Vardenafil treatment for erectile dysfunction. Ann Pharmacother. 2004;38:77–85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1345/aph.1D019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources