Effective biosonar echo-to-clutter rejection ratio in a complex dynamic scene
- PMID: 26328724
- PMCID: PMC4552698
- DOI: 10.1121/1.4915001
Effective biosonar echo-to-clutter rejection ratio in a complex dynamic scene
Abstract
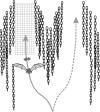
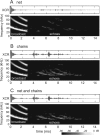
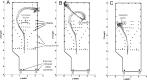
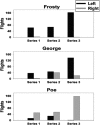
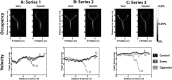
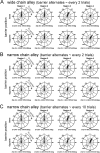
Biosonar guidance in a rapidly changing complex scene was examined by flying big brown bats (Eptesicus fuscus) through a Y-shaped maze composed of rows of strongly reflective vertical plastic chains that presented the bat with left and right corridors for passage. Corridors were 80-100 cm wide and 2-4 m long. Using the two-choice Y-shaped paradigm to compensate for left-right bias and spatial memory, a moveable, weakly reflective thin-net barrier randomly blocked the left or right corridor, interspersed with no-barrier trials. Flight path and beam aim were tracked using an array of 24 microphones surrounding the flight room. Each bat flew on a path centered in the entry corridor (base of Y) and then turned into the left or right passage, to land on the far wall or to turn abruptly, reacting to avoid a collision. Broadcasts were broadly beamed in the direction of flight, smoothly leading into an upcoming turn. Duration of broadcasts decreased slowly from 3 to 2 ms during flights to track the chains' progressively closer ranges. Broadcast features and flight velocity changed abruptly about 1 m from the barrier, indicating that echoes from the net were perceived even though they were 18-35 dB weaker than overlapping echoes from surrounding chains.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spatial memory and stereotypy of flight paths by big brown bats in cluttered surroundings.J Exp Biol. 2013 Mar 15;216(Pt 6):1053-63. doi: 10.1242/jeb.073197. J Exp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23447667
-
Effects of competitive prey capture on flight behavior and sonar beam pattern in paired big brown bats, Eptesicus fuscus.J Exp Biol. 2010 Oct 1;213(Pt 19):3348-56. doi: 10.1242/jeb.044818. J Exp Biol. 2010. PMID: 20833928 Free PMC article.
-
Interpulse interval modulation by echolocating big brown bats (Eptesicus fuscus) in different densities of obstacle clutter.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2009 Jun;195(6):603-17. doi: 10.1007/s00359-009-0435-6. Epub 2009 Mar 26. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19322570
-
Representation of perceptual dimensions of insect prey during terminal pursuit by echolocating bats.Biol Bull. 1996 Aug;191(1):109-21. doi: 10.2307/1543071. Biol Bull. 1996. PMID: 8776847 Review.
-
Temporal binding of neural responses for focused attention in biosonar.J Exp Biol. 2014 Aug 15;217(Pt 16):2834-43. doi: 10.1242/jeb.104380. J Exp Biol. 2014. PMID: 25122915 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Processing of Naturalistic Echolocation Signals in Bats.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 May 18;16:899370. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.899370. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 35664459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive computational model of animal biosonar signal processing.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Feb 17;17(2):e1008677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008677. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33596199 Free PMC article.
-
Avoidance of non-localizable obstacles in echolocating bats: A robotic model.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Dec 19;15(12):e1007550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007550. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31856162 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal patterning of acoustic gaze in echolocating bats navigating gaps in clutter.iScience. 2021 Mar 23;24(4):102353. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102353. eCollection 2021 Apr 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33870143 Free PMC article.
-
Spike Train Similarity Space (SSIMS) Method Detects Effects of Obstacle Proximity and Experience on Temporal Patterning of Bat Biosonar.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Feb 8;12:13. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00013. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29472848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gillette, M. D. , and Silverman, H. F. (2008). “ A linear closed-form algorithm for source localization from time-differences of arrival,” IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 15, 1–4.10.1109/LSP.2007.910324 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

