Tet-mediated imprinting erasure in H19 locus following reprogramming of spermatogonial stem cells to induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 26328763
- PMCID: PMC4556992
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13691
Tet-mediated imprinting erasure in H19 locus following reprogramming of spermatogonial stem cells to induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
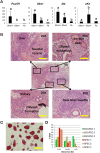
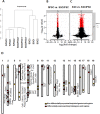
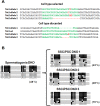
Selective methylation of CpG islands at imprinting control regions (ICR) determines the monoparental expression of a subset of genes. Currently, it is unclear whether artificial reprogramming induced by the expression of Yamanaka factors disrupts these marks and whether cell type of origin affects the dynamics of reprogramming. In this study, spermatogonial stem cells (SSC) that harbor paternalized imprinting marks, and fibroblasts were reprogrammed to iPSC (SSCiPSC and fiPSC). The SSCiPSC were able to form teratomas and generated chimeras with a higher skin chimerism than those derived from fiPSC. RNA-seq revealed extensive reprogramming at the transcriptional level with 8124 genes differentially expressed between SSC and SSCiPSC and only 490 between SSCiPSC and fiPSC. Likewise, reprogramming of SSC affected 26 of 41 imprinting gene clusters known in the mouse genome. A closer look at H19 ICR revealed complete erasure in SSCiPSC in contrast to fiPSC. Imprinting erasure in SSCiPSC was maintained even after in vivo differentiation into teratomas. Reprogramming of SSC from Tet1 and Tet2 double knockout mice however lacked demethylation of H19 ICR. These results suggest that imprinting erasure during reprogramming depends on the epigenetic landscape of the precursor cell and is mediated by TETs at the H19 locus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ferguson-Smith A. C. & Surani M. A. Imprinting and the epigenetic asymmetry between parental genomes. Science 293, 1086–1089 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Labosky P. A., Barlow D. P. & Hogan B. L. Mouse embryonic germ (EG) cell lines: transmission through the germline and differences in the methylation imprint of insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (Igf2r) gene compared with embryonic stem (ES) cell lines. Development 120, 3197–3204 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Wilmut I., Schnieke A. E., McWhir J., Kind A. J. & Campbell K. H. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature 385, 810–813 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

