A new approach to the problem of bulk-mediated surface diffusion
- PMID: 26328814
- PMCID: PMC4552701
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4928741
A new approach to the problem of bulk-mediated surface diffusion
Abstract
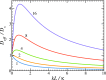
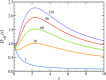
This paper is devoted to bulk-mediated surface diffusion of a particle which can diffuse both on a flat surface and in the bulk layer above the surface. It is assumed that the particle is on the surface initially (at t = 0) and at time t, while in between it may escape from the surface and come back any number of times. We propose a new approach to the problem, which reduces its solution to that of a two-state problem of the particle transitions between the surface and the bulk layer, focusing on the cumulative residence times spent by the particle in the two states. These times are random variables, the sum of which is equal to the total observation time t. The advantage of the proposed approach is that it allows for a simple exact analytical solution for the double Laplace transform of the conditional probability density of the cumulative residence time spent on the surface by the particle observed for time t. This solution is used to find the Laplace transform of the particle mean square displacement and to analyze the peculiarities of its time behavior over the entire range of time. We also establish a relation between the double Laplace transform of the conditional probability density and the Fourier-Laplace transform of the particle propagator over the surface. The proposed approach treats the cases of both finite and infinite bulk layer thicknesses (where bulk-mediated surface diffusion is normal and anomalous at asymptotically long times, respectively) on equal footing.
Figures



References
-
- Berg O. G., Winter R. B., and Vonhippel P. H., Trends Biochem. Sci. 7, 52 (1982).10.1016/0968-0004(82)90075-5 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

