Motor System Reorganization After Stroke: Stimulating and Training Toward Perfection
- PMID: 26328881
- PMCID: PMC4556825
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00014.2015
Motor System Reorganization After Stroke: Stimulating and Training Toward Perfection
Abstract
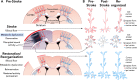
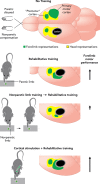
Stroke instigates regenerative responses that reorganize connectivity patterns among surviving neurons. The new connectivity patterns can be suboptimal for behavioral function. This review summarizes current knowledge on post-stroke motor system reorganization and emerging strategies for shaping it with manipulations of behavior and cortical activity to improve functional outcome.
©2015 Int. Union Physiol. Sci./Am. Physiol. Soc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
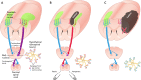
References
-
- Adkins DL, Bury SD, Jones TA. Laminar-dependent dendritic spine alterations in the motor cortex of adult rats following callosal transection and forced forelimb use. Neurobiol Learn Mem 78: 35–52, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Adkins DL, Boychuk J, Remple MS, Kleim JA. Motor training induces experience-specific patterns of plasticity across motor cortex and spinal cord. J Appl Physiol 101: 1776–1782, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Adkins DL, Campos P, Quach D, Borromeo M, Schallert K, Jones TA. Epidural cortical stimulation enhances motor function after sensorimotor cortical infarcts in rats. Exp Neurol 200: 356–370, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

