The Physiology of Fear: Reconceptualizing the Role of the Central Amygdala in Fear Learning
- PMID: 26328883
- PMCID: PMC4556826
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00058.2014
The Physiology of Fear: Reconceptualizing the Role of the Central Amygdala in Fear Learning
Abstract
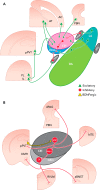
The historically understood role of the central amygdala (CeA) in fear learning is to serve as a passive output station for processing and plasticity that occurs elsewhere in the brain. However, recent research has suggested that the CeA may play a more dynamic role in fear learning. In particular, there is growing evidence that the CeA is a site of plasticity and memory formation, and that its activity is subject to tight regulation. The following review examines the evidence for these three main roles of the CeA as they relate to fear learning. The classical role of the CeA as a routing station to fear effector brain structures like the periaqueductal gray, the lateral hypothalamus, and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus will be briefly reviewed, but specific emphasis is placed on recent literature suggesting that the CeA 1) has an important role in the plasticity underlying fear learning, 2) is involved in regulation of other amygdala subnuclei, and 3) is itself regulated by intra- and extra-amygdalar input. Finally, we discuss the parallels of human and mouse CeA involvement in fear disorders and fear conditioning, respectively.
©2015 Int. Union Physiol. Sci./Am. Physiol. Soc.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- al Maskati HA, Zbrozyna AW. Stimulation in prefrontal cortex area inhibits cardiovascular and motor components of the defence reaction in rats. J Auton Nerv Syst 28: 117–125, 1989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH071537/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL-107675-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH096764/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH102191/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH-102191/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH-071537/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH-096764/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P51OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P51RR000165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL107675/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

