Diagnostic and prognostic value of bladder cancer-related transcript markers in urine
- PMID: 26328914
- PMCID: PMC11819347
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-015-2037-8
Diagnostic and prognostic value of bladder cancer-related transcript markers in urine
Abstract
Purpose: Since cytology as the current "gold standard" for noninvasive detection of bladder cancer (BCa) is characterized by a relatively low sensitivity, urinary transcript levels of survivin (SVV), Ki-67 and cytokeratin 20 (CK20) were evaluated as alternative or complementary biomarkers. Furthermore, their prognostic value was investigated.
Methods: Voided urine samples from 105 BCa patients and 156 controls were included. Total RNA was isolated from urine pellets and reverse-transcribed into cDNA. Expression levels of SVV, Ki-67 and CK20 were determined by quantitative PCR and normalized to the housekeeping gene TBP. Diagnostic performance of transcript markers and cytology was assessed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses. The prognostic value of the transcript markers was calculated by Cox proportional hazards models.
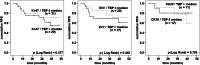
Results: ROC analyses resulted in AUC values between 0.71 (Ki-67) and 0.86 (CK20), indicating an appropriate diagnostic power. Using specifically defined cutoff values, the expression levels of the assessed biomarkers were significantly higher in urine specimens from BCa patients compared to control group (Mann-Whitney U test p < 0.001). Specificity ranged from 75% (SVV) to 84% (CK20) and sensitivity from 56% (Ki-67) to 87% (CK20). In combination with cytology, the sensitivity increased up to 97% (CK20). With regard to prognostic power, only SVV showed a significant, but not independent impact on the risk of recurrence (p = 0.008).
Conclusions: Quantitative assessment of tumor-related transcript markers, particularly of CK20, may serve as a noninvasive method to identify patients with BCa. Moreover, SVV appears to be useful as a marker for a high risk of recurrence.
Keywords: BIRC5; CK20; Ki-67; Survivin; Urine; Urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akobeng AK (2007) Understanding diagnostic tests 3: receiver operating characteristic curves. Acta Paediatr. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2006.00178.x - PubMed
-
- Al-Maghrebi M, Kehinde EO, Kapila K, Anim JT (2012) Urinary survivin mRNA expression and urinary nuclear matrix protein 22 BladderChek(R) and urine cytology in the detection of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Med Princ Pract. doi:10.1159/000334811 - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Comperat E, Sylvester RJ, Kaasinen E, Bohle A, Palou Redorta J, Roupret M (2013) EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.06.003 - PubMed
-
- Bassily NH, Vallorosi CJ, Akdas G, Montie JE, Rubin MA (2000) Coordinate expression of cytokeratins 7 and 20 in prostate adenocarcinoma and bladder urothelial carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. doi:10.1309/G1RA-EU9X-X6VV-3W79 - PubMed
-
- Christoph F, Weikert S, Wolff I, Schostak M, Tabiti K, Muller M, Miller K, Schrader M (2007) Urinary cytokeratin 20 mRNA expression has the potential to predict recurrence in superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.12.038 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

