Segmented slant hole collimator for stationary cardiac SPECT: Monte Carlo simulations
- PMID: 26328991
- PMCID: PMC4545103
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4928484
Segmented slant hole collimator for stationary cardiac SPECT: Monte Carlo simulations
Abstract
Purpose: This work is a preliminary study of a stationary cardiac SPECT system. The goal of this research is to propose a stationary cardiac SPECT system using segmented slant-hole collimators and to perform computer simulations to test the feasibility. Compared to the rotational SPECT, a stationary system has a benefit of acquiring temporally consistent projections. The most challenging issue in building a stationary system is to provide sufficient projection view-angles.
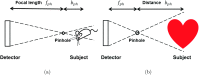
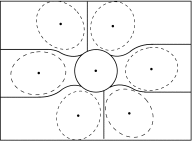
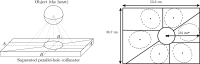
Methods: A GATE (GEANT4 application for tomographic emission) Monte Carlo model was developed to simulate a two-detector stationary cardiac SPECT that uses segmented slant-hole collimators. Each detector contains seven segmented slant-hole sections that slant to a common volume at the rotation center. Consequently, 14 view-angles over 180° were acquired without any gantry rotation. The NCAT phantom was used for data generation and a tailored maximum-likelihood expectation-maximization algorithm was used for image reconstruction. Effects of limited number of view-angles and data truncation were carefully evaluated in the paper.
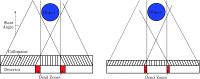
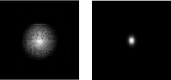
Results: Simulation results indicated that the proposed segmented slant-hole stationary cardiac SPECT system is able to acquire sufficient data for cardiac imaging without a loss of image quality, even when the uptakes in the liver and kidneys are high. Seven views are acquired simultaneously at each detector, leading to 5-fold sensitivity gain over the conventional dual-head system at the same total acquisition time, which in turn increases the signal-to-noise ratio by 19%. The segmented slant-hole SPECT system also showed a good performance in lesion detection. In our prototype system, a short hole-length was used to reduce the dead zone between neighboring collimator segments. The measured sensitivity gain is about 17-fold over the conventional dual-head system.
Conclusions: The gate Monte Carlo simulations confirm the feasibility of the proposed stationary cardiac SPECT system with segmented slant-hole collimators. The proposed collimator consists of combined parallel and slant holes, and the image on the detector is not reduced in size.
Figures








References
-
- Patton J. et al. , “D-SPECT: A new solid state camera for high speed molecular imaging,” J. Nucl. Med. 47(Suppl. 1), 189P (2006).
-
- Babla H., Bai C., and Conwell R., “A triple-head solid state camera for cardiac single photon emission tomography (SPECT),” Proc. SPIE 6319, 63190M–1–63190M–4 (2006). 10.1117/12.683765 - DOI
-
- http://cardiarc.com/cardiarc_scanner.html, accessed April 23, 2012.
-
- Liu Z., Kastis G. A., Stevenson G. D., Barrett H. H., Furenlid L. R., Kupinski M. A., Patton D. D., and Wilson D. W., “Quantitative analysis of acute myocardial infarct in rat hearts with ischemia-reperfusion using a high-resolution stationary SPECT system,” J. Nucl. Med. 43(7), 933–939 (2002). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

