Induction and Expression of Fear Sensitization Caused by Acute Traumatic Stress
- PMID: 26329286
- PMCID: PMC4677128
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2015.224
Induction and Expression of Fear Sensitization Caused by Acute Traumatic Stress
Abstract
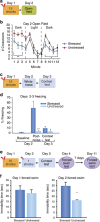
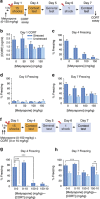
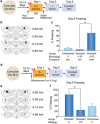
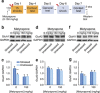
Fear promotes adaptive responses to threats. However, when the level of fear is not proportional to the level of threat, maladaptive fear-related behaviors characteristic of anxiety disorders result. Post-traumatic stress disorder develops in response to a traumatic event, and patients often show sensitized reactions to mild stressors associated with the trauma. Stress-enhanced fear learning (SEFL) is a rodent model of this sensitized responding, in which exposure to a 15-shock stressor nonassociatively enhances subsequent fear conditioning training with only a single trial. We examined the role of corticosterone (CORT) in SEFL. Administration of the CORT synthesis blocker metyrapone prior to the stressor, but not at time points after, attenuated SEFL. Moreover, CORT co-administered with metyrapone rescued SEFL. However, CORT alone without the stressor was not sufficient to produce SEFL. In these same animals, we then looked for correlates of SEFL in terms of changes in excitatory receptor expression. Western blot analysis of the basolateral amygdala (BLA) revealed an increase in the GluA1 AMPA receptor subunit that correlated with SEFL. Thus, CORT is permissive to trauma-induced changes in BLA function.
Figures
References
-
- Adamec R, Blundell J, Burton P (2005). Role of NMDA receptors in the lateralized potentiation of amygdala afferent and efferent neural transmission produced by predator stress. Physiol Behav 86: 75–91. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual V. American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC.
-
- Antoni FA (1986). Hypothalamic control of adrenocorticotropin secretion: advances since the discovery of 41-residue corticotropin-releasing Factor. Endocr Rev 7: 351–378. - PubMed
-
- Baker DG, West SA, Nicholson WE, Ekhator NN, Kaschow JW, Hill KK et al (1999). Serial CSF corticotropin-releasing hormone levels and adrenocortical activity in combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry 156: 585–588. - PubMed
-
- Bonne O, Grillon C, Vythilingam M, Neumeister A, Charney DS (2004). Adaptive and maladaptive psychobiological responses to severe psychological stress: implications for the discovery of novel pharmacotherapy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28: 65–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

