E6 and E7 gene silencing results in decreased methylation of tumor suppressor genes and induces phenotype transformation of human cervical carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 26329329
- PMCID: PMC4695162
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4525
E6 and E7 gene silencing results in decreased methylation of tumor suppressor genes and induces phenotype transformation of human cervical carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
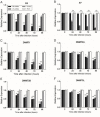
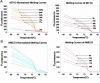
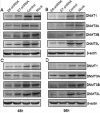
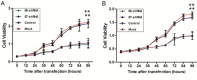
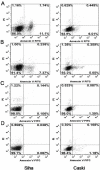
In SiHa and CaSki cells, E6 and E7-targeting shRNA specifically and effectively knocked down human papillomavirus (HPV) 16 E6 and E7 at the transcriptional level, reduced the E6 and E7 mRNA levels by more than 80% compared with control cells that expressed a scrambled-sequence shRNA. E6 and E7 repression resulted in down-regulation of DNA methyltransferase mRNA and protein expression, decreased DNA methylation and increased mRNA expression levels of tumor suppressor genes, induced a certain apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in E6 and E7 shRNA-infected SiHa and CaSki cells compared with the uninfected cells. Repression of E6 and E7 oncogenes resulted in restoration of DNA methyltransferase suppressor pathways and induced apoptosis in HPV16-positive cervical carcinoma cell lines. Our findings suggest that the potential carcinogenic mechanism of HPV16 through influencing DNA methylation pathway to activate the development of cervical cancer exist, and maybe as a candidate therapeutic strategy for cervical and other HPV-associated cancers.
Keywords: DNA methylation; HPV16 E6 and E7; cell viability and apoptosis; human cervical carcinoma cell lines; immunoblot.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Torre L.A, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Parkin D.M, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, et al. Inhibition of cervical cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by lentiviral-vector mediated shRNA targeting the common promoter of HPV16 E6 and E7 oncogenes. Antiviral Research. 2013;98:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Rampias T, et al. E6 and E7 Gene Silencing and Transformed Phenotype of Human Papillomavirus 16-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer Cells. JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2009;101:412–423. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, et al. Transcriptional gene silencing of HPV16 E6/E7 induces growth inhibition via apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Gynecologic Oncology. 2012;124:296–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

