Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 and Adiponectin and Associations with Muscle Deficits, Disease Characteristics, and Treatments in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 26329340
- PMCID: PMC4809051
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.150280
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 and Adiponectin and Associations with Muscle Deficits, Disease Characteristics, and Treatments in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with low muscle mass and density. The objective of our study was to evaluate associations between 2 serum biomarkers [insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and adiponectin] and skeletal muscle in RA.
Methods: Whole-body dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measures of the appendicular lean mass index (ALMI; kg/m(2)) and total fat mass index (kg/m(2)), as well as the peripheral quantitative computed tomography measures of the lower leg muscle and fat cross-sectional area (CSA; cm(2)) and muscle density (an index of fat infiltration) were obtained from 50 participants with RA, ages 18-70 years. Multivariable linear regression analyses evaluated associations between body composition and levels of adiponectin and IGF-1, adjusted for age, sex, and adiposity.
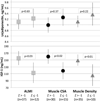
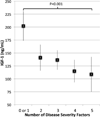
Results: Greater age was associated with higher adiponectin (p = 0.06) and lower IGF-1 (p = 0.004). Eight subjects had IGF-1 levels below the reference range for their age and sex. These subjects had significantly lower ALMI and muscle CSA in multivariable models. Lower IGF-1 levels were associated with greater clinical disease activity and severity, as well as low ALMI, muscle CSA, and muscle density (defined as 1 SD below normative mean). After adjusting for age and sex, greater adiponectin levels were associated with lower BMI (p = 0.02) as well as lower ALMI, and lower muscle CSA, independent of adiposity (p < 0.05). Only greater Health Assessment Questionnaire scores were significantly associated with lower adiponectin levels.
Conclusion: Low IGF-1 and greater adiponectin levels are associated with lower muscle mass in RA. Lower IGF-1 levels were seen in subjects with greater disease activity and severity.
Keywords: ADIPONECTIN; CACHEXIA; LEAN MASS; RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS.
Figures
References
-
- Walsmith J, Roubenoff R. Cachexia in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Cardiol. 2002;85:89–99. - PubMed
-
- Perrini S, Laviola L, Carreira MC, Cignarelli A, Natalicchio A, Giorgino F. The GH/IGF1 axis and signaling pathways in the muscle and bone: mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and osteoporosis. J Endocrinol. 2010;205:201–210. - PubMed
-
- Shefer G, Benayahu D. The effect of exercise on IGF-I on muscle fibers and satellite cells. Front Biosci. 2012;4:230–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
