Keratinocytes can modulate and directly initiate nociceptive responses
- PMID: 26329459
- PMCID: PMC4576133
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.09674
Keratinocytes can modulate and directly initiate nociceptive responses
Abstract
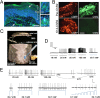
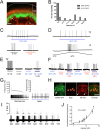
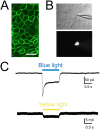
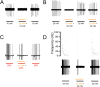
How thermal, mechanical and chemical stimuli applied to the skin are transduced into signals transmitted by peripheral neurons to the CNS is an area of intense study. Several studies indicate that transduction mechanisms are intrinsic to cutaneous neurons and that epidermal keratinocytes only modulate this transduction. Using mice expressing channelrhodopsin (ChR2) in keratinocytes we show that blue light activation of the epidermis alone can produce action potentials (APs) in multiple types of cutaneous sensory neurons including SA1, A-HTMR, CM, CH, CMC, CMH and CMHC fiber types. In loss of function studies, yellow light stimulation of keratinocytes that express halorhodopsin reduced AP generation in response to naturalistic stimuli. These findings support the idea that intrinsic sensory transduction mechanisms in epidermal keratinocytes can directly elicit AP firing in nociceptive as well as tactile sensory afferents and suggest a significantly expanded role for the epidermis in sensory processing.
Keywords: epidermal; keratinocyte; mouse; neuroscience; nociceptor; optogenetics; pain; sensory neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Baumbauer K, DeBerry JJ, Adelman P, Miller R, Davis BM, Albers KM, Koerber HR. Optical stimulation of keratinocytes activates cutaneous nociceptors. Washington, D.C.: Society for Neuroscience; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AR063772/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS073548/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS023725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS023725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS033730/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050758/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK063922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS023725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS075760/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS075760/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063772/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK101681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069951/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR066371/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS033730/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS050758/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AR066371/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK063922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

