CD4(+)CD25(High) Treg cells in HIV/HTLV co-infected patients with neuropathy: high expression of Alpha4 integrin and lower expression of Foxp3 transcription factor
- PMID: 26329520
- PMCID: PMC4557637
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-015-0116-x
CD4(+)CD25(High) Treg cells in HIV/HTLV co-infected patients with neuropathy: high expression of Alpha4 integrin and lower expression of Foxp3 transcription factor
Abstract
Background: Regulatory CD4 T cells (Tregs) are critical in maintaining the homeostasis of the immune system. Quantitative or phenotypic alterations and functional impairment of Tregs have been associated with the development of pathologies including those of the central nervous system. Individuals with HIV-1/HTLV-1 co-infection are more prone to develop neurological complications. The aim of this study was to characterize phenotypically Treg cells in HIV-1/HTLV-1 co-infected Mozambican individuals presenting neurological symptoms.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among HIV-infected individuals presentingneurological symptoms, with and without HTLV co-infection, and blood donors. Peripheral bloodmononuclear cells were stained with monoclonal antibodies conjugated with fluorochromes to quantifyTregs and activated T cells by four colors flow cytometry.
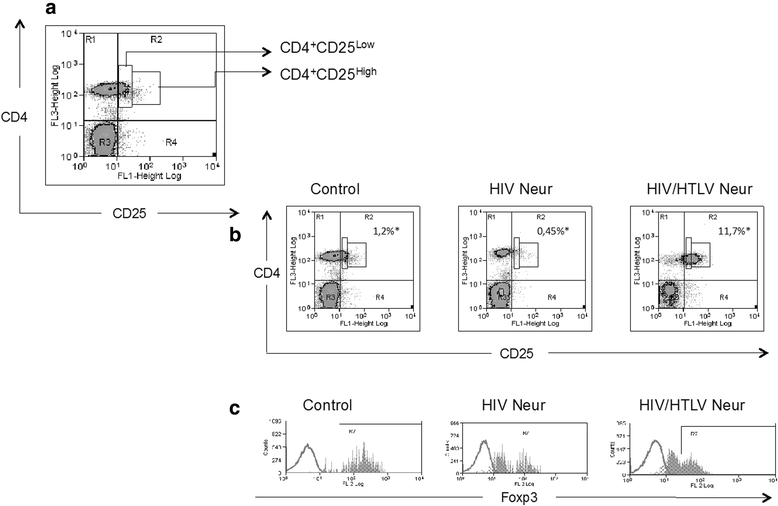
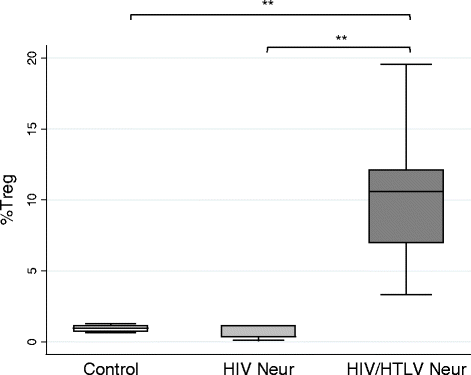
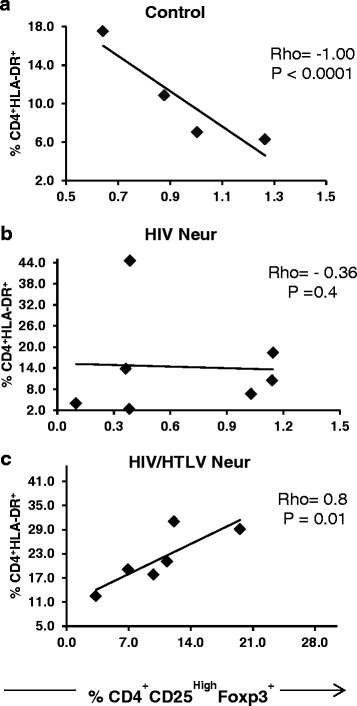
Results: Higher Treg cell frequency (10.6%) was noted in HIV-1/HTLV-1 co-infected group with neurological symptoms when compared to HIV-1 mono-infected group with neurological symptoms (0.38%, p = 0.003) and control group (0.9%, p = 0.0105). An inverse correlation between Foxp3 and CD49d expression was observed in all study groups (rh = -0.71, p = 0.001). In addition, increased levels of Treg cells in co-infected patients were strongly associated with total activated CD4 T cells (rh = 0.8, p = 0.01).
Conclusion: Treg cells in co-infected patients present phenotypic alterations and might have dysfunction marked by low expression of Foxp3 and increased expression of molecules not frequently seen on Treg cells, such as CD49d. These alterations may be related to (1) changes in Treg cell trafficking and migration, possibly making those cells susceptible to HIV infection, and (2) inability to control the activation and proliferation of effector T lymphocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Casseb J, de Oliveira AC, Vergara MP, Montanheiro P, Bonasser F, Meilman Ferreira C, et al. Presence of tropical spastic paraparesis/human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-associated myelopathy (TSP/HAM)-like among HIV-1-infected patients. J Med Virol. 2008;80(3):392–398. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21111. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tulius Silva M, de Melo EO, Bezerra Leite AC, Araujo A. Neurological aspects of HIV/human T lymphotropic virus coinfection. AIDS Rev. 2009;11(2):71–78. - PubMed
-
- Gudo ES, Bhatt NB, Bila DR, Abreu CM, Tanuri A, Savino W, et al. Co-infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1): does immune activation lead to a faster progression to AIDS? BMC Infect Dis. 2009;9:211. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-211. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

